Online Courses
Online CPD 2024 Calendar of Events
april 2024

Course Details
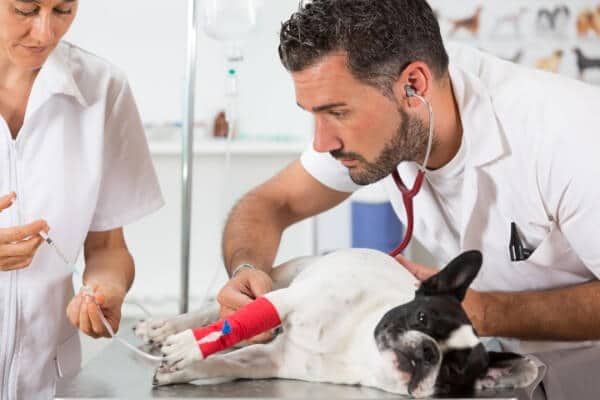
Week 1 Acute Kidney Injury Learning objectives After completion of this week, participants should be able to: Describe the functional anatomy of the kidney Understand and assess the
Course Details
Week 1
Acute Kidney Injury
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe the functional anatomy of the kidney
Understand and assess the origin of azotaemia in dogs and cats
Break down the terminology and pathophysiology of an acute kidney injury
Appreciate the clinical signs and tips on differentiating between AKI and CKD renal biomarkers and the importance of urinalysis for assessing renal function
Understand the nursing care that accompanies an AKI patient, including ins and outs, fluid therapy and the importance of bodyweight
Design a treatment plan for an AKI patient, including an in depth understanding of why we perform each task
Week 2
The Blocked Cat
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand predisposing factors to the blocked feline patient
Recognise the most common clinical signs and presentation of these cases
Understand and be able to perform the initial diagnostic procedures commonly performed
Recognise the hyperkalaemic patient and understand the treatment required
Demonstrate an understanding of the treatment options available for these cases
Identify different types of urinary catheters used in feline patients
Explain the nursing considerations of these patients
Week 3
Chronic Kidney Disease
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the difference between CKD and AKI
Discuss the clinical signs, why they manifest and what we can do to provide supportive treatment to the CKD patient
Talk about the laboratory findings including electrolytes and how/when we should intervene
Break down urinalysis and what it can tell us
Understand the pathology behind hypertension in CKD patients, the side effects and how to achieve accurate measurements
Identify useful nurse clinic tips for CKD patients
Week 4
Laboratory Diagnostics in Renal and Urinary Patients
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Recognise the common haematological, biochemical and electrolyte changes seen in patients with renal disease
Understand the International Renal Interest Society (IRIS) staging for chronic kidney disease
Explain the three key components of a urinalysis
Describe the classifications of proteinuria and understand possible underlying causes
Identify urinary crystals via microscopy
Understand external laboratory diagnostics to include: symmetric dimethylarginine and urine culture
Localise azotaemia in canine and feline patients
This course will be fully tutored by Charlotte Fennell and Sophie McMurrough and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
april 1 (Monday) – 26 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speakers for this event
-
Charlotte Fennell
Charlotte Fennell
BSc (Hons), CertVNECC, RVN, VTS (SAIM)
Senior Internal Medicine Nurse, Southfields Veterinary Specialists
BSc (Hons), CertVNECC, RVN, VTS (SAIM)
-
Sophie McMurrough
Sophie McMurrough
RVN, VTS (SAIM)
Head Medicine Nurse, Northwest Veterinary Specialists
RVN, VTS (SAIM)

Course Details
Week 1 Aetiology and Pathogenesis Anatomy of the head Tooth and periodontal anatomy, and oral soft tissues Oral nomenclature Tooth types, nomenclature and formulae Eruption times Occlusion Learning objectives After completion of
Course Details
Week 1
Aetiology and Pathogenesis
Anatomy of the head
Tooth and periodontal anatomy, and oral soft tissues
Oral nomenclature
Tooth types, nomenclature and formulae
Eruption times
Occlusion
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify tooth and periodontal structures
Explain the Modified Triadan System of numbering teeth in the dog and cat
Recognise normal occlusion
Week 2
Periodontology
Aetiology and pathogenesis of dental disease
Gingivitis
Periodontitis
Gingivostomatitis
Periodontal therapy
Scaling and polishing
Pocket control and therapy
Medications, homecare (brief), dental clinics (brief)
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe how gingivitis develops and its progression to periodontal disease
Explain what gingivostomatitis is
Outline the process of safe ultrasonic tooth scaling and its purpose
Week 3
Oral Pathology and Treatment
Trauma and treatment options
Tooth fracture / discolouration / (sub) luxation
Dental diseases and treatment options
Tooth resorption / caries / periodontal disease
Malocclusion and treatment options
Traumatic / dental / skeletal malocclusions
Other conditions and treatment options
Enamel defects / dentigerous cysts / persistent deciduous / root dilacerations and abnormal morphology / tumours
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify common pathologies associated with the teeth and oral cavity
Describe some potential treatment options for common pathologies
Week 4
Oral Examination and Charting
History taking and clinical examination – conscious oral examination
Pre-operative tests
Assessment under general anaesthesia – including anaesthesia induction, intubation, oral preparation, probing
Charting – what to fill in, disease scoring and making your chart work
Imaging and other investigations
Radiography – parallel and bisecting angle techniques
Biopsy
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Confidently undertake a thorough conscious examination of a patient’s teeth
and oral cavity
Set up for and assist with assessment of the teeth and oral cavity in an anaesthetised patient
Accurately complete a dental chart which documents all pathology discovered upon examination
Week 5
Instrumentation and Dental Surgery
Instruments – use, care and maintenance
Dental machine and other powered equipment – use, care and maintenance
Ancillary equipment – use, care and maintenance
Preparation for and veterinary nursing assistance with surgery
Pre-, intra- and post-operatively, including analgesia
The role of intraoperative radiography
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Differentiate between different instruments used for dental and oral procedures, and state what they are used for
Describe the proper use, care and maintenance of a range of dental instruments and equipment
Explain the benefits of oral radiography in veterinary patients and outline the basic, fundamental principles of the parallel and bisecting angle techniques
Week 6
Dental Clinics, Products and Homecare
What is an effective dental clinic
Types of patients attending dental clinics
Resources for dental clinic consultations
Products and interventions available to help with maintaining oral health
Oral homecare regimes
Effective dissemination of theoretical and practical oral hygiene advice
Client concordance and follow-up
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Debate what makes a dental clinic effective
Explain the range of resources required to run an effective dental clinic, and the purpose of these resources
Describe how a range of products and interventions used to maintain optimal oral health work
Outline how to achieve and maintain client compliance with recommended oral homecare regimes
The course will be fully tutored by Claire Bloor and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case scenarios, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
April 8 (Monday) – May 17 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Claire BloorClaire Bloor MA Ed, BSc (Hons) VN, RVN, PGCE, QTLS, Cert VN (Dent), IQA Veterinary Senior Lecturer – School of Veterinary Medicine, University of Central Lancashire
Course Details
Of the numerous cancers that affect our feline companions, lymphoma, squamous cell carcinoma, soft tissue sarcoma and mammary tumours are the most frequently diagnosed in the veterinary clinic. This 4 week
Course Details
Of the numerous cancers that affect our feline companions, lymphoma, squamous cell carcinoma, soft tissue sarcoma and mammary tumours are the most frequently diagnosed in the veterinary clinic.
This 4 week course dedicates a week per subject, where we explore the risk factors associated with each of these neoplasms and investigate the methods used to acquire a diagnosis. Treatment options will be discussed with particular detail placed on medical and surgical management techniques that can be applied to general practice and specialist nursing alike.
After completing this online course, participants will have a greater knowledge of these common diseases, enabling understanding of the prognosis and treatment goals; ultimately broadening communication and practical skills in the subject area.
This course is particularly suitable for nurses who have experience in oncology and are looking to broaden their knowledge and compliments the ‘Common Canine Cancer’ course with particular focus on feline friendly care. For nurses in general practice, the course ‘Introduction to Oncology’ may be more suitable.
Week 1
Mammary Tumours
Mammary tumours are a common tumour in cats which are often malignant, yet a small percentage are benign. Early detection and intervention can have a positive outcome and some patients go on to live disease-free lives, others require continuous treatment and monitoring.
Presentation and behaviour of mammary tumours
Diagnosis and staging
Treatment modalities and monitoring considerations
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Explain the potential causes of mammary tumours in cats
List what investigative procedures may be necessary to secure a diagnosis and what safety factors should be observed when sampling masses
Understand which treatment modalities are most useful for which form of the disease
Describe the patient and client care considerations when managing cases of feline mammary tumours
Week 2
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphocytes and/or lymphoid tissue, which is present in many locations within the body; presentation and treatment of these cases is dependant on location. This week we will cover:
Manifestation of feline lymphoma and categories of disease
Diagnosis, staging and prognostic indicators
Treatment options for feline lymphoma
Chemotherapy protocols, client expectations and how to create a feline friendly environment
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List the common manifestations of feline lymphoma and the patient groups most affected
Understand the value of staging and monitoring the disease
Describe the subtypes of feline lymphoma and the difference in treatment approaches
Explain the rationale of a multimodal chemotherapy protocol and how it may impact on prognosis
Analyse personal skill set and determine how you could support feline patients with lymphoma using your practice facilities
Week 3
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common form of head and mouth cancer in cats; the behaviour of this neoplasm is sometimes unpredictable and can be very invasive. On week three we discuss the presentation, investigation and treatment options available for these patients and look at some practices which are novel to veterinary medicine.
Presentation, diagnosis and staging of squamous cell carcinoma, including lymph node mapping
Treatment options and impact on prognosis
Surgical interventions, nursing support and rehabilitation
Introduction to electrochemotherapy and photodynamic therapy
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe the different imaging techniques used to evaluate feline squamous cell carcinoma
List treatment options and prognostic indicators for feline squamous cell carcinoma
Understand the mechanism of action behind novel techniques for feline squamous cell carcinoma
Describe the common surgical interventions and post-operative patient considerations
Week 4
Soft Tissue Sarcoma
Feline injection site sarcoma (FISS) is one of the most common soft tissue sarcomas of cats. The disease may present as a minor mass to the owner but often this is just the tip of the iceberg. Week 4 looks at FISS in more detail and brings the courses learning materials all together in this last week
Soft tissue sarcoma pathophysiology overview
Diagnostic and staging processes
Treatment options, radiation and surgical management
Adjuvant (post-operative) chemotherapy and restaging
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe the diagnostic approach to determining cancer diagnosis and tumour burden
Explain typical neoplastic behaviour of FISS and the impact of intervention on survival time
Understand the fundamental reasoning for adjuvant chemotherapy and the options for post-operative care
The course will be fully tutored by Nicola Read, and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
April 22 (Monday) – May 17 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Nicola ReadDipAVN (Medical), PgCert Veterinary Oncology, AFHEA, RVN Head Oncology Nurse, Royal Veterinary College

Course Details
This 4 week course will cover a range of clinical nutritional issues commonly encountered in first opinion practice. These will include those animals (feline and canine) with renal
Course Details
This 4 week course will cover a range of clinical nutritional issues commonly encountered in first opinion practice. These will include those animals (feline and canine) with renal disease, liver compromise, gastrointestinal disturbances, pancreatitis and urinary issues.
We will cover inappetence in animals and how to support these animals. We will investigate the route cause of inappetence and how pharmaceutical and nutritional support can aid in increasing calorific and nutrient intake. In all of these cases we will be looking at the evidence base behind the claims of diets and supplements and whether they are of benefit to our patients.
We will look at nutritional fashions and how to talk to clients about new trends that seem to be highlighted on-line almost continually. In order to do this we will have some case studies to work through where we can discuss different options to the nutritional management.
Week 1
Nutritional Assessment and Calculations
How to perform a nutritional assessment
Calculate energy requirements and how much to feed
Treatment regimens for inappetence
Instigating nutritional support
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Perform a nutritional history and assessment of the animal
Calculate BER and RERs and apply this to how much to feed
Identify when nutritional support is required and how to do this
Week 2
Clinical Nutrition – Renal, Urinary, Liver and Cardiac
Clinical nutrition for renal, urinary, liver and cardiac disease
Look at each of the nutrient requirements for each of these management regimes
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Make recommendations for clinical diets for renal, urinary, liver and cardiac disease
Understand the nutrient specifications for these diets
Discuss the benefits of these diets
Week 3
Clinical Nutrition – Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic
Clinical nutrition for gastrointestinal and pancreatitis
Look at each of the nutrient requirements for each of these management regimes
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Make recommendations for clinical diets for range of gastrointestinal and pancreatitis
Understand the nutrient specifications for these diets
Discuss the benefits of these diets
Week 4
Nutritional Supplements and Trends
Supplements
Nutritional trends (including raw and homecooked diets)
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Make recommendations for supplements for the diseases discussed in weeks 3 and 4
Look at the nutritional evidence behind nutritional fashions
Discuss raw and home cooked feeding with clients
The course will be fully tutored by Nicola Lakeman and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
April 22 (Monday) – May 17 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Nicola LakemanMSc, BSc(Hons), RVN, CertVNECC, CertSAN, VTS(Nutrition) Nutrition Manager, IVC Evidensia

Course Details
Week 1 Performance Reviews and Appraisals This first week, we will look at how to conduct appraisals and performance reviews. We will look at the different styles
Course Details
Week 1
Performance Reviews and Appraisals
This first week, we will look at how to conduct appraisals and performance reviews. We will look at the different styles of checklists and forms that can be used to conduct these sessions, and we will discuss how to give feedback, whether good or bad. We will look at how performance reviews can be used to help with staff members who are not performing at an expected level.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Know how to give constructive feedback
How to set performance action plans
Design an appraisal form, in order to conduct an appraisal
Week 2
Quality Improvement
QI is an important part of clinical practice and it often lands on veterinary nurses to conduct clinical audits. We will explore what QI involves, how to develop evidence-based practice, what a journal club is, and how to implement clinical audits.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the concepts of clinical governance, quality improvement and clinical audits
How to implement a clinical audit
Understand how to start a journal club
Week 3
Disciplinary Issues
We will look at what to do if you have a situation when a staff member that doesn’t arrive to work on time, has performance issues, or doesn’t comply to rules. We will look at how you can manage these people, how to set reviews and action plans, along with what to do if they don’t adhere to these action plans.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Set action plans and how to review these
Know how to conduct an investigation into conduct
Understand what the disciplinary process involves
Week 4
Finances
Part of being a head nurse is also knowing how the business works – having a basic understanding of how your role as head nurse affects profit/loss is important. Stock control, purchasing, pricing and charging correctly are a vital part of this
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the importance of stock control and how to implement a simple system to aid your stock takes
Understand the importance of charging and how making a few changes can make a difference
Know why it is important to charge for your time
The course will be fully tutored by Nicola Lakeman, and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
April 22 (Monday) – May 17 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Nicola LakemanMSc, BSc(Hons), RVN, CertVNECC, CertSAN, VTS(Nutrition) Nutrition Manager, IVC Evidensia
Course Details
Week 1 Approach to the Caesarean Patient Brief overview of parturition Complications of parturition Caesarean section Learning objectives After completion of this week,
Course Details
Week 1
Approach to the Caesarean Patient
Brief overview of parturition
Complications of parturition
Caesarean section
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Explain complications that might occur in parturition
Explain the reasons for intervening in these cases in order to perform a C section
Understand nursing of the caesarean patient
Week 2
The GDV Patient
Physiology of GDV
Diagnosis
Stabilisation of the GDV
Anaesthesia considerations
Post-operative nursing
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the physiology of a GDV and list some of the common risk factors associated with this condition
Describe how a GDV is diagnosed and which tests can help us to identify this condition in the emergency patient
List the common stabilisation techniques in the emergency patient including management of shock and commonly used gastric decompression techniques
Discuss anaesthesia considerations and how to make the patient a safe candidate for surgery
Describe the nursing considerations for the post-operative GDV case and the factors which need to be included in the care plan of the hospitalised patient
Week 3
Nursing the Septic Abdomen Patient
What are SIRS and sepsis?
Recognising sepsis
The use of diagnostic tools in the veterinary practice to help recognise a septic abdomen
Nursing management of a septic abdomen
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe SIRS and sepsis and the difference between them
Understand how to recognise sepsis in veterinary patients
List the different tests we have available in practice that can be used to help identify a septic abdomen
Explain how patients with a septic abdomen can best be nursed in practice, pre-, peri and post operatively
Week 4
Haemoabdomen
Physiology of haemoabdomen
Diagnosis
Stabilisation of the haemoabdomen
Anaesthesia considerations
Post-operative nursing
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the physiology of a haemoabdomen and list some of the common causes associated with this condition
Describe how a haemoabdomen is diagnosed and which tests can help us to identify this condition in the emergency patient
List the common stabilisation techniques in the emergency patient including management of shock
Discuss anaesthesia considerations and how to make the patient a safe candidate for surgery
Describe the nursing considerations for the post-operative haemoabdomen case and the factors which need to be included in the care plan of the hospitalised patient
The course will be fully tutored by Elle Haskey and Katie Gray and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
April 29 (Monday) – May 24 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speakers for this event
-
Elle Haskey
Elle Haskey
BSc(hons), VTS(ECC) VPAC A1, RVN
HEAD EMERGENCY AND CRITICAL CARE NURSE, ROYAL VETERINARY COLLEGE
BSc(hons), VTS(ECC) VPAC A1, RVN
-
Katie Gray
Katie Gray
Dip AVN, RVN
SENIOR EMERGENCY AND CRITICAL CARE NURSE, ROYAL VETERINARY COLLEGE
Dip AVN, RVN
Course Details
Week 1 Physiotherapy Toolkit (Modalities) Electrotherapies Therapeutic hot/cold packs Manual therapies Applied exercise therapies Learning objectives After completion of this week, participants should be able to: Understand the principles and application
Course Details
Week 1
Physiotherapy Toolkit (Modalities)
Electrotherapies
Therapeutic hot/cold packs
Manual therapies
Applied exercise therapies
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the principles and application of electrotherapy including:
K-laser
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES)
Pulsed magnetic therapy (Biomag)
Therapeutic ultrasound
Understand the use of therapeutic hot/ cold packs
Understand manual therapy and its application including:
Massage
Effleurage
Coupage
Joint mobilisations
Graded stretches
Understand applied exercise therapy including:
Strengthening and stabilising exercises
Balance and proprioceptive exercises
Functional exercises
Hydrotherapy
Week 2
Patient Assessment
Musculoskeletal patient assessment
Neurological patient assessment
Respiratory / critical care patient assessment
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Carry out a basic musculoskeletal, neurological, and respiratory physiotherapy assessment
Understand valid outcome measures to guide patient treatment
How to write SOAP (subjective, objective, analysis, plan) notes to progress patient treatment
Week 3
Physiotherapy and Hydrotherapy Treatment Techniques
Early phase rehabilitation 0-2 weeks
Mid phase rehabilitation 2-6 weeks
Late phase rehabilitation 6-12 weeks
Patient discharge or maintenance physiotherapy programme
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Carry out early physiotherapy treatment including:
Early manual therapy techniques
Early phase hot and cold pack treatment
Early electrotherapies to improve healing and for pain relief
Mid phase gentle exercise programmes including hydrotherapy
Late phase exercise therapy to include advanced strengthening, proprioceptive, balance and functional exercises
Late phase electrotherapies for pain relief, soft tissue injuries and muscle strengthening
Week 4
Physiotherapy Progression Plans and Home Exercise Programmes
Patient rehabilitation plans
Discharge and maintenance programmes
Home exercise plans
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Learn how and when to progress patient plans from early to mid through to late stage rehabilitation to optimise patient outcomes
Understand when to discharge a patient, or to continue with a maintenance programme for chronic cases or surgical complications
Design home exercise programmes for owners to carry out
Week 5
Musculoskeletal Case Studies
CCL reconstruction – TPLO or lateral suture
Soft tissue injuries (tendinopathies, iliopsoas strains)
Fracture repair
Conservative management of chronic conditions, including hip dysplasia and elbow dysplasia
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Consider appropriate assessment, treatment plan and progression of a musculoskeletal case study
Consider appropriate assessment, treatment plan and progression of a soft tissue case study
Consider appropriate assessment, treatment plan and progression of a fracture repair case study
Consider appropriate assessment, treatment plan and progression of a chronic condition case study
Week 6
Neurological and Respiratory (Intensive Care) Case Studies
Hemi- laminectomy (HLE)
Fibrocartilage embolism (FCE)
Pneumonia
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Consider appropriate assessment, treatment plan and progression of a surgical neurological case study
Consider appropriate assessment, treatment plan and progression of a non-surgical case study
Consider appropriate assessment, treatment plan and progression of a respiratory (critical care) case study
This course will be fully tutored by Donna Carver, and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
April 29 (Monday) – June 7 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Donna CarverBSC(Hons) Physiotherapy, DipAVN (Surgical), RVN, MCSP Pain & Rehabilitation Service, Glasgow Veterinary School
may 2024
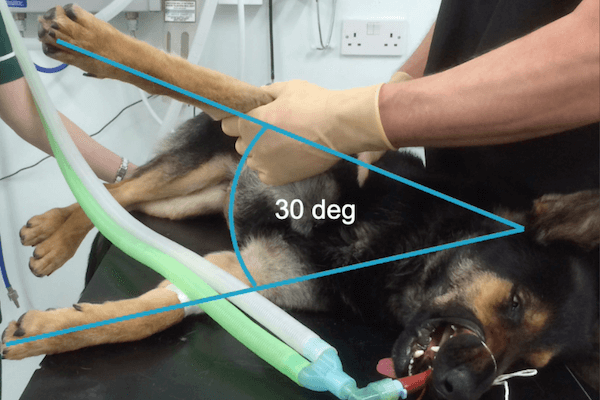
Course Details
Course Summary This 30 minute eCPD tutorial is designed to help nurses understand the diagnosis, imaging and surgical treatment options for shoulder lameness in the dog. Conditions covered include: Medial
Course Details
Course Summary
This 30 minute eCPD tutorial is designed to help nurses understand the diagnosis, imaging and surgical treatment options for shoulder lameness in the dog. Conditions covered include:
Medial shoulder instability
Supraspinatus / infraspinatus contracture
Osteochondrosis, osteochondritis dissecans
Ruptured lateral glenohumeral ligament
Bicipital tenosynovitis / rupture
Course Tutor
Chris Morris BVSc CertSAS MRCVS
Referral Surgeon, Dovecote
Course Length
The course is worth 30 minutes of CPD for UK delegates and 0.5 AVNAT points for Australian and New Zealand delegates
The course is provided with unlimited lifetime access for on-demand learning
Course Notes
Unfortunately, course notes are not available with this tutorial
Release date: May 2024
Time
may 1 (Wednesday) – 31 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Chris MorrisBVSc CertSAS MRCVS Dovecote Referrals
Course Details
Week 1 Monitoring Modalities There are many advanced monitoring tools and nursing interventions that can be used in our patients, however, a key part of this is
Course Details
Week 1
Monitoring Modalities
There are many advanced monitoring tools and nursing interventions that can be used in our patients, however, a key part of this is deciding when it is appropriate to employ them. We will discuss and compare different monitoring tools that we have available, including:
Blood pressure monitoring – invasive versus non-invasive
Central venous pressure
ECG
Blood gases – venous versus arterial
We will also explore when these monitoring tools may be beneficial compared with when their use might be contraindicated.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Determine which patients would benefit from more intensive monitoring
Understand how to conduct each kind of monitoring and explain the information we can obtain
Understand the difference between arterial blood pressure monitoring and central venous pressure
Understand the complications of using the more invasive monitoring tools
Week 2
Tubes and Drains
Various tubes and drains are commonly used in critically ill ICU patients, and it is vital we understand how to manage these safely and effectively. We will look at a variety of different tubes and drains including Jackson Pratt drains and active grenades, thoracic tubes, tracheostomy tubes and pericardiocentesis catheters among others.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the different drains and their functions
Safely manage and nurse patients with various types of tubes
Understand the complications that may occur with various interventions
Confidently troubleshoot drain management
Week 3
Cardiovascular Support
Sometimes fluids just aren’t enough! There are a variety of issues we can encounter with our critically ill patients and cardiovascular support and monitoring becomes an important aspect of the RVN’s role. We will look at the different causes of cardiovascular instability and how we can address those including the use of vasopressors and inotropes.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the methods of monitoring that can assist with determining both low and high-volume states
Identify cases where the use of vasopressors and inotropes are indicated
Explain the different conditions that lead to changes in cardiovascular function
Understand the ECG assessment and recognise the main life threatening abnormalities
Week 4
Constant Rate Infusions
Constant rate infusions are commonly used in the ICU, and it is really useful for RVN’s to be able to calculate these dosages. Whilst the maths can sometimes seem baffling, if you understand the basics, it is a very useful skill. CRIs are very beneficial for many of our patients and are attainable in any practice with an infusion pump.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Calculate ANY CRI from scratch!
Understand the benefits and issues associated with use of CRIs
Understand multimodal analgesia options for critically ill patients
The course will be fully tutored by Kath Howie and will consist of 10 hours of CPD and will be provided in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case scenarios, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
May 20 (Monday) – June 14 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Kath HowieVTS (ECC), RVN Principal Nurse Manager, Vets Now
june 2024
Course Details
Week 1 Vascular Access Indications for IV placement Different types of IV catheter Different placement techniques IV catheter management Complications Learning objectives After completion of this week, participants should be able
Course Details
Week 1
Vascular Access
Indications for IV placement
Different types of IV catheter
Different placement techniques
IV catheter management
Complications
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List the indications and contraindications for IV catheter placement
Understand the difference between peripheral and central venous catheterisation
Describe the different IV catheter options currently on the veterinary market and their placement technique
Discuss how to manage IV catheters – both peripheral and central
Describe the common complications associated with IV catheters and how to minimise them
Week 2
Urinary Catheters
Indications for placing urinary catheters
Different types of urinary catheters
Placement of urinary catheters
Urinary catheter management
Complications
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List the indications and contraindications for urinary catheter placement
Describe the different urinary catheter options currently for veterinary use
Explain how urinary catheters are placed
Discuss how to manage urinary catheters in practice
Describe the common complications associated with urinary catheters
Week 3
Chest Drains
When chest drains are placed
Different types of chest drain
Different placement techniques
Chest drain management
Complications
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List the indications and contraindications for chest drain placement
Describe the different chest drain options currently on the veterinary market and their placement techniques
Explain how to drain the chest drain and what options are available should the patient have a continuous pneumothorax
Discuss how to manage the chest drain and how to identify a drain that is ready for removal
Describe the common complications associated with chest drains and how to minimise them
Week 4
Tracheostomy Tubes
Indications for tracheostomy tube placement
Different types of tracheostomy tubes
Placement of tracheostomy tubes
Management of tracheostomy tubes
Complications
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List the indications and contraindications for placing tracheostomy tubes
Understand the different types of tracheostomy tubes available for veterinary use
Describe how tracheostomy tubes are placed
Explain how to manage tracheostomy tubes in situ
Describe the common complications associated with tracheostomy tubes in practice
The course will be fully tutored by Elle Haskey and Katie Gray, and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
june 3 (Monday) – 28 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speakers for this event
-
Elle Haskey
Elle Haskey
BSc(hons), VTS(ECC) VPAC A1, RVN
HEAD EMERGENCY AND CRITICAL CARE NURSE, ROYAL VETERINARY COLLEGE
BSc(hons), VTS(ECC) VPAC A1, RVN
-
Katie Gray
Katie Gray
Dip AVN, RVN
SENIOR EMERGENCY AND CRITICAL CARE NURSE, ROYAL VETERINARY COLLEGE
Dip AVN, RVN
Course Details
Week 1 Preparation and Monitoring of Critical Cases Preparedness Considerations Invasive blood pressure monitoring Blood gas analysis Spirometry Learning objectives After completion of this week, participants should be able to: List generalised
Course Details
Week 1
Preparation and Monitoring of Critical Cases
Preparedness
Considerations
Invasive blood pressure monitoring
Blood gas analysis
Spirometry
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List generalised considerations for preparing to anaesthetise emergency cases
Setup and use invasive blood pressure monitoring and how this relates to oscillometric and doppler techniques
Interpret a basic blood gas analysis and outline how this abnormality may have occurred
Explain what spirometry is and how it differs from capnography
Week 2
Abdominal Surgical Emergencies
Gastric dilatation and volvulus
Haemoabdomen
The acute abdomen
Epidural anaesthesia
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the physiological disturbances caused by gastric dilatation and volvulus
Understand the physiological disturbances caused by haemoabdomen
Understand the physiological disturbances caused by the acute abdomen
Suggest considerations for these surgeries and list possible complications that may arise during anaesthesia
List the total and relative contraindications for epidural anaesthesia
Week 3
Thoracic Surgical Emergencies
Pyothorax
Penetrating injuries
Diaphragmatic rupture
Mechanical ventilation
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the physiological disturbances caused by pyothorax
Understand the physiological disturbances caused by a penetrating injury
Understand the physiological disturbances caused by diaphragmatic rupture
Suggest considerations for these surgeries and list possible complications that may arise during anaesthesia
Feel confident to safely choose ventilator settings for use during non-emergency surgery
Week 4
Caesareans
Physiology
ASA categorisation
Anaesthesia protocols
Anaesthesia infusions (TIVA)
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the physiological considerations for caesarean section
Assign and justify the choice of an ASA category to the caesarean section patient
Suggest a safe protocol for caesarean section, with variation based on differing drug availability depending on clinical setting
Understand the basis of total intravenous anaesthesia infusions
Week 5
What’s Happening? What Should I do?
Hypoxia
Hypocapnia
Hypotension
ECG Abnormalities
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List possible causes of, and suggest treatments for hypoxia and hypocapnia
List possible causes of hypotension and discuss the physiology of both pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment options
Interpret the most common ECG abnormalities seen and understand how these rhythms will affect the patient, and have an understanding of possible treatment options
Week 6
CRASH!
Recover CPR guidelines
Crash box
Basic life support
Advanced life support
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List the vital components of a crash box
Perform safe and effective chest compressions in a variety of patient sizes and conformations
Understand how to monitor the effectiveness of CPR in the clinical setting
Interpret the most common ECG rhythms seen during CPR
Understand what drug treatment options are available during CPR
The course will be fully tutored by William McFadzean and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case scenarios, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
June 3 (Monday) – July 12 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
William McFadzeanBVetMed, CertAVP (VA), DipECVAA, MRCVS Cave Veterinary Specialists

Course Details
Week 1 Feline Heart Disease Prevalence, aetiology and pathophysiology of feline heart disease Classification systems used to diagnose and treat feline cardiomyopathies Nursing care and treatment aims Learning objectives
Course Details
Week 1
Feline Heart Disease
Prevalence, aetiology and pathophysiology of feline heart disease
Classification systems used to diagnose and treat feline cardiomyopathies
Nursing care and treatment aims
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Explain the pathophysiology of feline heart disease
Understand the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine (ACVIM) classification system as it applies to feline cardiomyopathies
Be familiar with the best approach to a nurse a cat with heart disease and heart failure
Week 2
Canine Heart Disease
Prevalence, aetiology and pathophysiology of myxomatous mitral valve disease (MMVD) and dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM)
Classification systems used to diagnose and treat MMVD
Staging systems used to diagnose and treat DCM in dogs
Nursing care of dogs with heart disease and heart failure
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Explain the pathophysiology of MMVD and DCM
Understand the ACVIM classification system as it applies to MMVD and the staging system as it applies to canine DCM
Be familiar with the best approach to nurse a dog with either MMVD or DCM
Week 3
Electrocardiography (ECG) – Theory
The ECG machine and settings
Achieving a good quality ECG trace
How to interpret an ECG
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Set up an ECG and understand the settings
Apply theory to achieve a good quality ECG trace
Understand how to interpret an ECG, using an algorithmic system
Week 4
Electrocardiography (ECG) – Application
Application of theory from week 1 to cases
Anaesthesia and ECGs
Life threatening arrhythmias
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Apply theoretical learning to practical cases
Understand the role of anaesthesia and surgery upon ECGs
Identify life threatening arrhythmias
Week 5
Heart Failure
Pathophysiology of heart failure
Acute life threatening and chronic management
Management of patients with heart failure
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand how heart failure can occur
Identify patients with heart failure and nurse them appropriately
Recognise drugs used in the treatment of heart failure
Week 6
Diagnostic Tests and the Cardiac Patient
Diagnostic tests used in cardiac patients
How to approach the test and the patient
Evaluation of diagnostic tests in cardiac patients
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Perform or assist with diagnostic tests with confidence
Apply best practice methods to achieve reliable and repeatable results
Understand the purpose of diagnostic tests used in cardiac medicine
The course will be fully tutored by Charlotte Pace and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case scenarios, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
June 10 (Monday) – July 19 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Charlotte PaceBA (Hons), RVN, VTS (Cardiology), PGCert (VetEd), FHEA
Course Details
Week 1 Preparing for Surgery Organisation of rooms and equipment in the theatre area Scheduling and planning surgical caseload Infection control related to the surgical theatre Preparation of the patient for surgery
Course Details
Week 1
Preparing for Surgery
Organisation of rooms and equipment in the theatre area
Scheduling and planning surgical caseload
Infection control related to the surgical theatre
Preparation of the patient for surgery
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the basics of infection control in the operating theatre
Identify the correct order of surgical procedures based on availability of equipment, personnel and rooms
Prepare the patient for a range of procedures, including preparation of skin, eyes and mucous membranes
Develop infection control protocols relating to procedure in their own practice
Week 2
The Theatre Nurse’s Role
Circulating nurse duties
Preparing the surgical team
Surgical hand preparation
Scrub nurse role
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the key qualities and requirements for the circulating nurse and scrub nurse roles
Identify the correct products and techniques for an effective surgical hand preparation and be able to demonstrate those
Choose appropriate protocols for the preparation of the surgical team
Correctly position patients for a range of surgical procedures
Week 3
Instrumentation and Sterilisation
Common surgical instrumentation
Taking care of your instruments and equipment
What happens after surgery!
Cleaning, disinfection, and sterilisation
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify common surgical instruments and understand their use
Develop the skills to take apart and reassemble surgical equipment for the cleaning process
Understand the key sterilisation techniques used in veterinary medicine
Week 4
Bringing it all Together – Surgical Skills for Nurses
Suture material – what to use and when??
Common suture patterns
Surgical skills
Developing the surgical nurse’s role in practice
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify properties of suture material and understand how that helps guide the choice of which one to use
Demonstrate common surgical suture patterns that could be performed by a veterinary nurse
Understand relevant surgical skills for veterinary nurses and how these can benefit your practice
The course will be fully tutored by Alison Young and will consist of 10 hours of CPD and will be provided in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case scenarios, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
June 17 (Monday) – July 12 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Alison YoungDipAVN (Surgical), VTS (Surgery), RVN Head Theatre Nurse, Royal Veterinary College
Course Details
Cats are living longer, and with the cat pet population increasing, it’s even more important that our ageing cats are seen regularly at the clinic. Older cats present with a
Course Details
Cats are living longer, and with the cat pet population increasing, it’s even more important that our ageing cats are seen regularly at the clinic. Older cats present with a special set of challenges, and the veterinary nurse plays a key part in monitoring and caring for these patients right through to end of life.
Week 1
Age Related Disease and Nursing Considerations
Age related diseases commonly seen in cats from the age of 7 years upwards
Findings from the Feline Healthy Ageing Clinic
How nursing care differs in ageing cats
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Be aware of commonly seen age related diseases
Adapt nursing care for the ageing patient
Prepare hospitalisation for the ageing cat
Week 2
Creating and Running Ageing Cat Clinics
How to set up and run ageing cat clinics
Owner education and compliance
Feline friendly handling for the ageing patient
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Create and run ageing cat clinics
Create an owner questionnaire
Understand the importance of owner education
Adapt handling skills to suit the ageing patient
Week 3
Nutritional Considerations
Nutrition for ageing life stages
Nutrition for specific age related disease
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Make nutritional recommendations for the ageing cat
Make nutritional recommendations for age related diseases
Discuss the benefits of different diets and nutrient specifications
Week 4
Quality of Life and End of Life Care
Quality of life tools
Supporting the palliative patient
Euthanasia considerations
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the importance of using quality of life tools
Feel confident using quality of life tools
Communicate sensitively to owners surrounding end of life
Carry out euthanasia with consideration for the patient as well as the owner
This course will be fully tutored by Kelly Eyre and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
June 17 (Monday) – July 12 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Kelly EyreRVN, ISFM DipFN, AdvCertFB Clinical Lead, Royal Canin Feline Healthy Ageing Clinic, University of Liverpool
july 2024
Course Details
Week 1 Radiation Physics and Safety Learning objectives After completion of this week, participants should be able to: Understand the properties of x-rays Explain how an x-ray tube
Course Details
Week 1
Radiation Physics and Safety
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the properties of x-rays
Explain how an x-ray tube works
Explain how digital x-ray systems work
Explain the risks of working with radiation
Explain the principles of radiation protection and how this is implemented in veterinary practice
Week 2
Radiographic Anatomy and Physiology in Small Animal Patients
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the normal radiographic anatomy of the thorax
Understand the normal radiographic anatomy of the abdomen
Understand the normal radiographic anatomy of the spine
Understand the normal radiographic anatomy of the thoracic limb
Understand the normal radiographic anatomy of the pelvis and pelvic limbs
Week 3
Radiographic Techniques (Positioning and Contrast Studies)
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand and implement the optimum positioning for thoracic radiographs
Understand and implement the optimum positioning for abdominal radiographs
Understand and implement the optimum positioning for spinal radiographs
Understand and implement the optimum positioning for pelvic
Understand and implement the optimum positioning for thoracic limb radiographs
Understand and implement the optimum positioning for pelvic limb radiographs
Explain specialised orthopaedic views (TTA / TPLO / stressed / flexed / extended)
Understand contrast media and its usage
Describe contrast and dynamic studies (IVU / retrograde urethrocystogram/angiography)
Week 4
MRI and CT – Physics and Safety
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe the basic principles of how CT works
Describe the basic principles of how MRI works
Explain safety concerns when working with CT
Explain safety concerns when working with MRI
Compare differences between CT and MRI
Week 5
MRI Techniques and Acquisition
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand how to position small animal patients for spinal imaging
Understand how to position small animal patients for brain imaging
Explain which sequences are commonly utilised in small animal imaging
Understand commonly seen MRI artefacts
Week 6
CT Techniques and Acquisition
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand how to position small animal patients for commonly performed CT studies (Spine / Thorax / Abdomen / Elbow)
Explain which reconstruction algorithms can be utilised and when
Understand commonly seen CT artefacts
This course will be fully tutored by Ash Moors and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
July 15 (Monday) – August 23 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Ash MoorsFdSc, GradDipVN, PGCertVedEd, FHEA, RVN VETERINARY RADIOGRAPHER ROYAL VETERINARY COLLEGE

Course Details
Week 1 Feline Cardiomyopathies Cardiovascular anatomy and physiology Common cardiomyopathies affecting cats Treatment of feline cardiomyopathies The owners role in monitoring cardiomyopathies Learning objectives After completion of this week, participants
Course Details
Week 1
Feline Cardiomyopathies
Cardiovascular anatomy and physiology
Common cardiomyopathies affecting cats
Treatment of feline cardiomyopathies
The owners role in monitoring cardiomyopathies
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe the normal physiology of the heart
Describe common disease processes which affect the feline heart
Understand the role of diet within feline cardiomyopathies
Discuss various treatment options available for feline cardiomyopathies
Understand the role nurses and owners can play in monitoring these cases
Week 2
Feline Triaditis
Brief review of gastrointestinal, pancreatic and hepatic anatomy and physiology
Pathophysiology of triaditis in the cat (inflammatory bowel disease, pancreatitis and cholangitis)
Advanced imaging and diagnostic techniques
Treatment options available both as an inpatient and an outpatient
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Discuss the disease process of triaditis including the associated clinical signs
Understand how nurses can support patients through advanced imaging (flexible endoscopy / abdominal ultrasound)
Understand how to assist with the collection of pathological samples in these cases
Discuss the long term management of triaditis and the potential for ongoing disease
Week 3
Feline Asthma
Overview of respiratory anatomy and physiology
Predisposed breeds
Computed tomography and bronchoscopy
Treatment of feline asthma
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe the clinical pathological changes associated with feline asthma
Discuss advanced imaging techniques that can be utilised in the work up of these cases
Confidently and competently support the general anaesthesia of a cat with respiratory disease
Discharge a patient to owners and confidently discuss the treatment of asthmatic cats
Week 4
Feline Infectious Peritonitis
The pathophysiology of FIP including both ‘wet’ and ‘dry’ forms
Transmission of FIP
Treatment options available for FIP
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the predisposing factors for the development of FIP
Discuss the clinical signs associated with FIP
Indicate the importance of infection control
Identify treatment options and protocols currently available
Advise owners how to limit the potential for disease transmission within households
This course will be fully tutored by Beth Thomas and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
July 29 (Monday) – August 23 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Beth ThomasVTS (SAIM), RVN Internal Medicine Nurse, VetsNow Manchester Referrals
Course Details
Week 1 Transfusion Medicine This week we will look at indications for packed red cell and whole blood transfusions, in both cats and dogs, in the acute
Course Details
Week 1
Transfusion Medicine
This week we will look at indications for packed red cell and whole blood transfusions, in both cats and dogs, in the acute emergency setting. The nurse’s role is vital in this field, including preparing the recipient, blood typing, cross matching and monitoring the recipient. We will cover common reasons for transfusion and patient specific nursing concerns, as well as indications for auto transfusion and xenotransfusion. Common coagulopathies will also be discussed, along with indications for the use of plasma products in small animal patients.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Select the correct blood product for the individual patient
Understand the monitoring these patients require and patient specific concerns
Explain the different transfusion reactions that can occur and how they are avoided and treated
List the indications for auto transfusion and xenotransfusion
Describe the main coagulopathies we encounter and the treatment options available
Week 2
Acute Kidney Injury
Acute kidney injury is a relatively common presentation in emergency and critical care, however, it can occur for a variety of reasons. This week will look at the conditions that lead to acute kidney injury and how we reach that diagnosis. We will look at treatment options including reviews of the evidence bases in terms of patients that are anuric. The nursing role in these patients is multi- faceted and it is vital we can monitor and nurse these patients effectively.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the different reasons that AKI develops, including post-surgery, toxin related and obstruction of the urinary tract
Understand the monitoring and nursing requirements of these patients including fluid therapy, acid-base status and how we recognize when they are deteriorating
Explain how we manage anuric patients including evidence reviews of methods to force diuresis
Understand the basics of peritoneal and haemodialysis for these patients and the indications
Week 3
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
DKA is a complex disorder that can be life threatening for our patients, and the nursing team play a large role in the management and recovery of these patients. There are multiple considerations in nursing a patient with DKA that go well beyond administering insulin. We will review common reasons for a patient to develop this endocrine disorder as well as acid- base and electrolyte abnormalities we may see.
These patients need intensive monitoring including repeated blood work so we will discuss how to minimize the impact of this on their welfare. There will also be discussion on the different approaches to administration of insulin and ongoing management of these cases when they are discharged home.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Recognise the concurrent conditions that may lead to difficulty stabilizing the DKA patient
Understand how we reach the diagnosis and the treatment priorities for these patients
Understand the different approaches to insulin administration as well as the pros and cons of each method
Explain how to prioritise appropriate monitoring for these patients
Week 4
Acute Pancreatitis
The pancreatitis patient is a common presentation to any practice. It is an inflammatory condition that can be classed from mild to severe. We will focus on the nursing care and assessment of the patients requiring hospitalisation for management. Whilst we often consider these patients as just needing a couple of days of supportive care, there are some serious complications that can occur and contribute to mortality.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand common aetiologies in dogs and cats
Review pain management options including drug types and routes of administration
Discuss nutritional support options
Identify complications including development of SIRS
Week 5
Acute Respiratory Distress
These patients present many challenges to us in practice and need some special consideration in terms of monitoring and nursing care. We will look at recognition of the patient in respiratory distress, the potential causes, and our priorities for treatment. We will review the monitoring tools that may be beneficial and our approach to stabilising these patients.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Prioritise stabilisation techniques based on patient presentation
Determine which method of oxygen supplementation is most appropriate for specific patients
Appreciate the management of patients in brachycephalic crisis
Understand the different approaches to diagnostics and monitoring for these very fragile patients
Week 6
Addisonian Crisis
Known as the “great pretender”, Addison’s disease leads to a potentially life-threatening situation when the patient goes into crisis. Whilst electrolyte abnormalities are present in a typical Addisonian we can see no electrolyte changes in atypical cases. The patient with an Addison’s crisis has multiple abnormalities which we need to monitor and correct. Consideration of management options for these patients as well as resolving the crisis will all be discussed.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the aetiology, common clinical signs, and effects of this complex disorder
Identify and differentiate a patient that has Addison’s disease, with a patient in an Addisonian crisis
Understand the nursing considerations for these patients in the hospital environment, and appreciate the impact stress hormones have
Identify priorities for treatment and ongoing management
This course will be fully tutored by Kath Howie and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
July 29 (Monday) – September 6 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Kath HowieVTS (ECC), RVN Principal Nurse Manager, Vets Now
august 2024
Course Details
Course Summary This eCPD tutorial will discuss the most common age related diseases we see in ageing cats, and provide information on setting up and running ageing cat clinics
Course Details
Course Summary
This eCPD tutorial will discuss the most common age related diseases we see in ageing cats, and provide information on setting up and running ageing cat clinics in practice. Running these clinics can help us to detect age related diseases early, helping us to improve the length and quality of life in our ageing cats.
Course Tutor
Kelly Eyre RVN, ISFM DipFN, AdvCertFB
Clinical Lead, Royal Canin Feline Healthy Ageing Clinic, University of Liverpool
Course Length
The course is worth 75 minutes of CPD for UK delegates and 1.25 AVNAT points for Australian and New Zealand delegates
The course is provided with unlimited lifetime access for on-demand learning
Course Notes
Unfortunately, course notes are not available with this tutorial
Release date: Aug 2024
Time
august 1 (Thursday) – 31 (Saturday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Kelly EyreRVN, ISFM DipFN, AdvCertFB Clinical Lead, Royal Canin Feline Healthy Ageing Clinic, University of Liverpool
Course Details
Week 1 Preparation, Priorities and Checklists Patient safety The anaesthesia plan and patient priorities Preparation and checklists Learning objectives After completion of this week, participants should be able to: Understand
Course Details
Week 1
Preparation, Priorities and Checklists
Patient safety
The anaesthesia plan and patient priorities
Preparation and checklists
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand how preparation and use of checklists improve patient safety
Prepare individual anaesthesia plans for sick patients and/or complex procedures
Understand how to prioritise important considerations
Understand how to prepare the patient and equipment to minimise harmful delays and mistakes
Construct and use relevant patient safety checklists
Week 2
Ventilation, Capnography and Neuromuscular Blockade
Physiology of spontaneous and controlled ventilation
Ventilators
Capnography
Neuromuscular blockade
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand in which situations it is appropriate to use controlled ventilation
Understand how to set up a ventilator and what all the buttons do!
Understand the physiology and technology of capnography
Understand how to interpret different capnograph traces
Understand how to use and monitor neuromuscular blocking drugs
Week 3
Advanced Monitoring and Cardiovascular Support
Physiology of heart rate and blood pressure
The electrocardiogram
Measuring blood pressure
Treating hypotension and arrhythmias
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Have a better understanding of ECG interpretation and when to worry
Understand how to interpret blood pressure measurements
Understand when and how to treat common arrhythmias
Understand different ways of treating hypotension
Week 4
Perioperative Analgesia
Analgesic drugs in the peri-anaesthetic period
Multimodal analgesia
Analgesic infusions
Using local anaesthetic techniques
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Have an understanding of the pharmacology of analgesic drugs
Understand which drugs are useful in which situations
Select and prepare analgesic drugs for intravenous infusions
Understand and select appropriate local anaesthetic techniques for different procedures
The course will be fully tutored by Colette Jolliffe and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
August 12 (Monday) – September 6 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Colette JolliffeBVetMed, CertVA, DipECVAA, FRCVS European and RCVS Recognised Specialist in Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia, Anderson Moores Veterinary Specialists

Course Details
Week 1 Patient Assessment and Triage The concept of triage Preparedness Primary survey Secondary Survey Emergency history Learning objectives After completion of this week, participants should be able to: Understand the triage
Course Details
Week 1
Patient Assessment and Triage
The concept of triage
Preparedness
Primary survey
Secondary Survey
Emergency history
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the triage process and how it can be utilised to prioritise emergency care
Describe how to make their team and environment prepared for when the emergency patient arrives
List how to carry out a primary survey during the initial assessment of the patient
Explain how to carry out a secondary survey assessment in order to list their concerns with the patient
Discuss how to communicate with the client including telephone advice, informed consent and emergency history
Week 2
Shock
Classify shock
Emergency database
Blood pressure
Oxygen therapy
The use of multiparameter monitors
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify a patient with shock and classify which type of shock they have
Explain which parameters may be tested during an emergency database and how these can help to identify shock in the emergency room
Understand the physiology of perfusion and ways in which blood pressure can be monitored in the emergency patient
List the different ways that oxygen therapy can be delivered to the emergency patient
Understand the uses and limitations of multiparameter monitors and their role in monitoring perfusion trends
Week 3
Fluid Therapy
Patient assessment
Identifying a fluid deficit or change in volume
What fluids are available
Managing a change in content
Identifying a change in fluid distribution
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Explain how to assess the patient’s fluid status using clinical exam and blood work
Discuss how to create a fluid plan to treat a fluid deficit such as hypovolaemia or dehydration
List what fluid options are available and which fluid might be preferred in which situation
Understand how fluid selection or the fluid plan can be altered to account for an electrolyte abnormality
Describe how to manage the patient with fluid overload or peripheral oedema
Week 4
Neurological Emergencies
Neurological assessment
Coma scoring
Raised intracranial pressure
Seizures
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe how to perform a neurological assessment of an emergency patient
Describe how to perform a coma score and understand how these may be used in neurological patients
Understand methods of identifying raised intracranial pressure and the physiology behind this
Recognise a seizuring patient and understand their management, from initial presentation and stabilisation of mild seizures through to the management of a patient in status epilepticus
Week 5
Approach to the Trauma Patient
Assessment of wounds
Wound management
Management of fractures
Other injuries associated with trauma
Analgesia
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify different wounds based on the patient history and appearance of the wound
Understand the principles of wound management and common techniques used to flush and debride wounds
Describe how to identify and manage fractures in the trauma patient
List other common injuries associated with trauma and how these should be managed
Implement an analgesia plan for the trauma patient based on pain assessment
Week 6
Common Toxicities
Common toxins seen in emergency practice
Renal toxins
Hepatotoxins
Anticoagulants
Neurotoxins
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe the different ways toxins can enter the body
List the most common renal toxins and understand the treatment of these patients
List the most common hepatotoxins and understand the different treatments for each of these
Understand the physiological effects of anticoagulant ingestion and the treatment of these patients
Identify the most common neurotoxins seen in practice and understand the treatment of these patients
The course will be fully tutored by Elle Haskey and Katie Gray and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
August 12 (Monday) – September 20 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speakers for this event
-
Elle Haskey
Elle Haskey
BSc(hons), VTS(ECC) VPAC A1, RVN
HEAD EMERGENCY AND CRITICAL CARE NURSE, ROYAL VETERINARY COLLEGE
BSc(hons), VTS(ECC) VPAC A1, RVN
-
Katie Gray
Katie Gray
Dip AVN, RVN
SENIOR EMERGENCY AND CRITICAL CARE NURSE, ROYAL VETERINARY COLLEGE
Dip AVN, RVN
september 2024
Course Details
Of the numerous cancers that affect our canine companions, lymphoma, mast cell tumours, oral melanoma and osteosarcoma are the most frequently diagnosed in the veterinary clinic. This 4 week
Course Details
Of the numerous cancers that affect our canine companions, lymphoma, mast cell tumours, oral melanoma and osteosarcoma are the most frequently diagnosed in the veterinary clinic.
This 4 week course dedicates a week per subject, where we explore the risk factors associated with each of these neoplasms and investigate the methods used to acquire a diagnosis. Treatment options will be discussed with particular detail placed on medical and surgical management techniques that can be applied to general practice and specialist nursing alike.
After completing this online course, participants will have a greater knowledge of these common diseases, enabling understanding of the prognosis and treatment goals; ultimately broadening communication and practical skills in the subject area.
This course is particularly suitable for nurses who have experience in oncology and are looking to broaden their knowledge. For nurses in general practice, the course ‘Introduction to Oncology’ may be more suitable.
Week 1
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphocytes and/or lymphoid tissue, which is present in many locations within the body, hence making the presentation of these cases typical or atypical depending on location. Specialist tests have been developed to categorise this cancer and treatment is determined by these findings.
Manifestation of lymphoma and categories of disease
Diagnosis, staging and specialist tests for lymphoma
Treatment options for lymphoma
Chemotherapy protocols, client expectations and the cancer journey
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List the common manifestations of canine lymphoma and the patient groups most affected.
Understand the value of specialist tests required to further categorise cancer
Describe the subcategories of lymphoma and the difference in treatment approaches
Explain the rationale of a multimodal chemotherapy protocol and how it may impact on prognosis
Analyse personal skill set and determine how you could support patients with lymphoma using your practice facilities
Week 2
Osteosarcoma
Canine osteosarcoma of the weight bearing bones often manifests in pain and/or lameness in affected patients. Once a diagnosis has been determined, the behaviour of this neoplasm is predictable, yet still individual to the animal.
Osteosarcoma pathophysiology overview
Diagnostic and staging processes
Treatment options, radiation and surgical management
Adjuvant (post-operative) chemotherapy and restaging
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe the diagnostic approach to determining cancer diagnosis and tumour burden
Explain typical neoplastic behaviour of canine osteosarcoma and how it is a model for comparative medicine
List the different treatment options and their impact on survival time
Understand the fundamental reasoning for adjuvant chemotherapy and the options for post-operative care
Week 3
Melanoma
Oral melanoma is the most common form of cancer of the mouth in dogs; there are various forms and the behaviour of this neoplasm is sometimes unpredictable. On week three we discuss the presentation, investigation and treatment options available for these patients and look at some practices which are novel to veterinary medicine.
Presentation, diagnosis and staging of oral melanoma, including lymph node mapping
Treatment options and impact on prognosis
Surgical interventions, nursing support and rehabilitation
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe the value of different tissue sampling and specialist imaging techniques
List treatment options and prognostic indicators for canine melanoma
Describe the surgical technique, complications and post-operative care required for oral melanoma cases
Understand the mechanism of action behind current research for canine melanoma and apply to evidence-based medicine within nursing practice
Week 4
Mast Cell Tumours
Mast cell tumours are a form of skin cancer in dogs, which depending on their grade and affected site, can have an impact on neoplastic behaviour and prognosis. Many patients go on to live disease-free lives, others require continuous treatment and monitoring.
Presentation and behaviour of mast cell tumours
Diagnosis, staging and specialised tests
Treatment modalities and monitoring considerations
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Explain which breeds of dogs are commonly affected by mast cell tumours and how the patient may present
List what investigative procedures may be necessary to secure a diagnosis and what safety factors should be observed when sampling masses
Describe which treatment modalities are most useful for which form of the disease
Understand the use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and “metronomic chemotherapy” as a method for controlling cancer growth
The course will be fully tutored by Nicola Read, and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
september 2 (Monday) – 27 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Nicola ReadDipAVN (Medical), PgCert Veterinary Oncology, AFHEA, RVN Head Oncology Nurse, Royal Veterinary College

Course Details
Week 1 Setting Up and Running Nurse Clinics Which clinics to run? Charging for clinics Standardisation of the clinics Client compliance How to increase client numbers Making recommendations Marketing and publicity Building confidence Reflective practice Learning
Course Details
Week 1
Setting Up and Running Nurse Clinics
Which clinics to run?
Charging for clinics
Standardisation of the clinics
Client compliance
How to increase client numbers
Making recommendations
Marketing and publicity
Building confidence
Reflective practice
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the consulting nurse’s pivotal role in practice
Appreciate the varying types of clinics nurses can offer
Learn how to increase numbers coming into clinics, and increase recommendations to the clinics
Understand how to increase client compliance in clinics
Know various ways to market and advertise the clinics on offer
Week 2
Consulting Skills
Communication in clinics
Consultation skills
Content of your clinic
Keeping to time
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the process of consulting
Understand the importance of communication, the customer journey and improving outcomes
Understand the importance of protocols for clinic content and the running of these clinics
Week 3
Lifestage Clinics
Puppy and kitten clinics
Senior clinics
Other lifestage clinics
What to include
Timings of clinics
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Timings of clinics and how these will improve client education and binding to the practice
Understand the content for these clinics and what to discuss with clients at this time
Understand the elements of preventative healthcare
Understand the importance of nutritional assessments in all of the nurse clinics
Week 4
Obesity and Mobility Clinics
Content of mobility and obesity clinics
Nutritional requirements for obesity
Client motivation
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the content to include for each of these clinics
Calculate feeding amounts, what treats (if any) we can feed and exercise regimes
Understand how environmental adaptations can improve QOL for our pets with mobility issues
Understand the role of supplements in these cases
Discuss methods of how to motivate clients
The course will be fully tutored by Nicola Lakeman, and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
september 2 (Monday) – 27 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Nicola LakemanMSc, BSc(Hons), RVN, CertVNECC, CertSAN, VTS(Nutrition) Nutrition Manager, IVC Evidensia
Course Details
Week 1 Pre-anaesthetic Assessment and Patient Preparation for Anaesthesia Patient preparation ASA status and patient assessment Use of checklists Breathing systems and checks What are the aims of anaesthetic premedication Practical considerations What agents are
Course Details
Week 1
Pre-anaesthetic Assessment and Patient Preparation for Anaesthesia
Patient preparation
ASA status and patient assessment
Use of checklists
Breathing systems and checks
What are the aims of anaesthetic premedication
Practical considerations
What agents are available
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Correctly identify an appropriate breathing system and safe fresh gas flow rates for individual patients
Confidently check an anaesthesia machine and breathing system to ensure they are safe to use
Have an understanding of the ASA grading system and be able to designate and apply which status is appropriate for their individual patients
Identify the benefits of using a peri-anaesthetic checklist and decide whether this can be advocated for their working environment
List the reasons for patient premedication and be able to identify practical aspects and factors within the clinic which may affect the efficacy of premedication
Identify the most common pharmacological agents used for sedation and anaesthesia
Week 2
Anaesthetic Monitoring – Neurological and Respiratory System
Basic, hands on monitoring (neurological system)
Respiratory monitoring
Other
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Recognise what are normal physiological parameters with regards to the neurological and respiratory systems for individual patients undergoing anaesthesia
Name the most common pieces of monitoring equipment for the respiratory system and be able to recognise what is a normal value/trace for each of these pieces
Start to develop the skills to apply this knowledge to individual cases within the clinic with use of the available equipment
Week 3
Anaesthetic Monitoring – Cardiovascular System
Cardiovascular monitoring
Basic, hands on
Blood pressure
Pulse oximetry
ECG
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Recognise what are normal physiological parameters with regards to the cardiovascular system for individual patients undergoing anaesthesia
Name the most common pieces of monitoring equipment for the cardiovascular system and be able to recognise what is a normal value/trace for each of these pieces
Start to develop the skills to apply this knowledge to individual cases within the clinic with use of the available equipment
Week 4
Principles of Perioperative Care including Anaesthetic Recovery
Anaesthetic risk
Airway management including tracheal intubation
Patient positioning
Eye care
Temperature
Fluid therapy
Patient recovery
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify important factors which require attention and care during a patient’s anaesthetic in order to optimise the patient’s peri-anaesthetic experience
Accurately calculate fluid rates for individual patients and apply this to their clinical setting, whether this be with use of fluid pumps/syringe drivers or via gravity (calculating a drop rate)
List available methods for patient warming, with recognition of the need to counteract patient hypothermia and the potential risks associated with warming device use
Recognise the critical importance of patient monitoring during anaesthetic recovery.
Describe the potential difficulties that may be encountered during the anaesthetic recovery period
Week 5
Pain Assessment
Importance of pain assessment and management
Challenges of pain assessment in veterinary species
Pain assessment tools
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Recognise the potential difficulties in performing pain assessment in veterinary species.
Name a number of pain assessment tools
Advocate a pain assessment tool that would be suitable for their working environment
Recognise when patients (cats and dogs) are deemed to be painful
Week 6
Analgesia for Acute Perioperative Pain
A brief overview on the pain pathway with introduction to the concepts of multimodal and pre-emptive analgesia
Analgesic options, including:
A brief overview of the pharmacological means
Non-pharmacological methods
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Explain why provision of analgesia is important for patient welfare
Describe the concepts of multimodal and pre-emptive analgesia, with emphasis on why these are important for patient analgesia
Explain why provision of analgesia is important
List potential analgesic options and apply this knowledge to consider appropriate therapeutic plans for individual patients
Have an appreciation of the important role that a veterinary nurse can play in providing non-pharmacological methods of analgesia and improving the patient experience
This course will be fully tutored by Becky Robinson and will consist of 15 hours of CPD (15 points for Australia and New Zealand) and will be provided in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
September 2 (Monday) – October 11 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Rebecca RobinsonBVSc, MVetMed, DipECVAA, FHEA, MRCVS EUROPEAN & RCVS SPECIALIST IN VETERINARY ANAESTHESIA, DAVIES VETERINARY SPECIALISTS
Course Details
Brachycephalic breeds have seen a huge surge in popularity in recent years, and we are now nursing these patients on a daily basis. These patients come with a
Course Details
Brachycephalic breeds have seen a huge surge in popularity in recent years, and we are now nursing these patients on a daily basis. These patients come with a whole host of breed specific problems, directly related to their anatomy, and this course aims to comprehensively cover all aspect of nursing brachycephalics in practice, including anaesthesia, medicine, surgery, critical care and our vitally important role in client education.
Week 1
An Introduction to Brachycephalics
Brachycephalic anatomy basics
Breeds commonly affected
Recent increase in popularity and the effects on the breed
Co-morbidities commonly seen in brachycephalics
Communication with owners
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Recognise and discuss the anatomy of a brachycephalic patient
Understand the causes that can be attributed to clinical signs often displayed by patients suffering with BOAS
Identify co-morbidities often diagnosed in brachycephalic patients
Understand when and why communication with owners about brachycephalic pet ownership is vital
Understand the Cambridge BOAS assessment
Week 2
Brachy Breathing – Crisis and Management
Triage
Respiratory sounds
Blood gas analysis
Aspiration pneumonia
Oxygen therapy
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand how to triage the brachycephalic patient
Recognise the difference between the various respiratory sounds
Identify the uses of blood gas analysis in respiratory conditions
Understand available treatments for aspiration pneumonia
Explain the different methods of providing oxygen therapy
Week 3
It’s a Hot Topic – Heatstroke Management
Heatstroke identification
Treatment options
Recovery process
Risks and complications
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify a patient at risk of heatstroke
Explain how to care for the hot brachycephalic
Understand the risks associated with heatstroke
List the clinical signs to look out for in a recovering heatstroke patient
Describe treatments for the recovering heatstroke patient with a secondary condition
Week 4
Brachycephalic Anaesthesia
Balanced anaesthesia plans
Anaesthetic equipment
Anaesthetic monitoring
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand how to perform a pre-anaesthetic evaluation
Design a patient specific anaesthesia plan, to include – premedication, induction, maintenance, and other medications to support the brachycephalic patient in the peri-anaesthesia period
Understand the approach to monitoring the brachycephalic patient under anaesthesia
Week 5
Managing a Difficult Airway
Pre-anaesthetic airway compromise and signs of potential difficult airways
Intubations, including tips and equipment aids
Ways to assist patient recovery from anaesthesia
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Evaluate a patient prior to anaesthesia to determine severity of airway compromise
Identify the clinical signs to alert the anaesthetist to a potential difficult airway prior to induction
List the different intubation aids and how to maximise successful intubations, to maintain oxygenation and minimise hypoxia.
Understand how we can assist recoveries in the brachycephalic patient to achieve extubation and reduce incidence of post anaesthesia respiratory obstruction
Week 6
Head and Neck Surgery
Preparing the patient for surgery
Surgical techniques to correct common conditions – stenotic nares, elongated soft palate, everted laryngeal saccules, everted palatine tonsils, skin fold resection and tracheotomy/tracheostomy
Surgical techniques for conditions affecting the eyes – canthoplasty, grafting for ulceration, entropion etc.
Instrumentation
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Prepare the patient for a range of procedures, including preparation of skin, eyes and mucous membranes
Correctly position patients for a range of surgical procedures involving the head and neck
Understand the most common surgical procedures, and explain these to owners
Tailor a post-operative care plan for each individual patient
Week 7
All the Other Problems Not in the Head and Neck!
Preparing the patient for surgery
Surgical techniques for a range of common conditions including caesarean sections, fracture repairs (humeral condyle), hiatus hernia, screw tail, hemilaminectomy and pulmonic stenosis
Instrumentation
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Prepare theatre and the patient for a range of surgical procedures
Understand the most common surgical procedures, and explain these to owners
Tailor a post-operative care plan for each individual patient
Identify common surgical instruments and understand their use
Week 8
Ophthalmology
Corneal ulceration, exposure keratopathy and corneal pigmentation
Corneal sequestrums in cats
Entropion and Ectropion
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS)
Tear overflow and staining
Proptosis
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Explain the common ocular conditions in the brachycephalic patient
Understand the treatment options for the above conditions
Feel more confident when nursing the ophthalmic patient and what specific considerations to bear in mind
This course will be fully tutored by Lydia Christie Woodend Smith, Katie Gray, Lisa Angell, Alison Young and Sian Woodham-Davies and will consist of 20 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. There will be two short written assignments for the course, one based on ECC and the other on an anaesthesia topic. This course is tutored for 8 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
September 2 (Monday) – October 25 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speakers for this event
-
Alison Young
Alison Young
DipAVN (Surgical), VTS (Surgery), RVN
Alison qualified as a veterinary nurse whilst working at a small practice in Hertfordshire. She joined the Queen Mother Hospital in 2001 as a general surgery nurse and worked rotating through all areas of the hospital. In 2003 she joined the theatre nursing team and studied for the Diploma in Advanced Veterinary Nursing (Surgical) where she gained the highest marks for that year. Alison gained the VTS (Surgery) in 2015 and is Head Theatre Nurse at the Royal Veterinary College.
DipAVN (Surgical), VTS (Surgery), RVN
-
Katie Gray
Katie Gray
Dip AVN, RVN
SENIOR EMERGENCY AND CRITICAL CARE NURSE, ROYAL VETERINARY COLLEGE
Dip AVN, RVN
-
Lisa Angell
Lisa Angell
VTS (anaesthesia and analgesia), PgCert Vet Ed, FHEA, RVN
VTS (anaesthesia and analgesia), PgCert…
-
Lydia Christie Woodend Smith
Lydia Christie Woodend Smith
RVN
RVN
-
Sian Woodham-Davies
Sian Woodham-Davies
RVN
RVN

Course Details
Week 1 Toxicology Introduction The top 10 commonly encountered toxins in small animal patients will be reviewed along with up-to-date evidence-based guidelines looking at treatment recommendations and options We will
Course Details
Week 1
Toxicology Introduction
The top 10 commonly encountered toxins in small animal patients will be reviewed along with up-to-date evidence-based guidelines looking at treatment recommendations and options
We will review the reported antidotes as well as the use of intra-lipid emulsion and other supportive measures we may implement in patients suffering from intoxication
Common complications of the various intoxications we can encounter will be reviewed as well as discussion of how we may pre-empt and manage these
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Recognise the main toxins we see in practice
Develop a systematic approach to the intoxicated patient
Discuss the evidence bases looking at use of activated charcoal, intra-lipids and other antidotes, along with supportive measures for the intoxicated patient
Appreciate the main complications we may encounter with an intoxicated patient Understand how to address and nurse intoxicated patients into recovery
Week 2
Central Nervous System Toxins
Detailed discussion of the toxins that commonly affect the central nervous system including recreational drugs, human medications, organic toxins, household, and environmental concerns
We will look at decontamination of these patients as well effective nursing care and monitoring for the patient with severe CNS depression associated with intoxication
Discuss when an antidote may be indicated and the systemic effects, we can see associated with CNS intoxications
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the effects of the main toxins affecting the CNS
Consider how to provide emergency treatment for these patients and also develop a plan for longer term care
Discuss whether decontamination is appropriate for patients when the CNS is depressed
Understand the complications and challenges we may encounter
Week 3
Renal System Toxins
Discuss toxins that affect the patient’s renal system including ethylene glycol, NSAID ingestion, Baclofen, raisins/grapes amongst others.
Consider how we can identify a patient with an acute kidney injury due to a toxin and the treatment options available, including peritoneal dialysis and haemodialysis amongst others
Nursing care for these patients is intensive and a focus on fluid balance and electrolyte status is vital, so this will be covered in detail
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the different toxins that affect the renal system and how we can approach nursing and monitoring these patients
Consider approaches to acid-base stabilisation and electrolyte abnormality management
Understand why volume overload occurs, and how we monitor, prevent and manage this condition
Week 4
Hepatic, Cardiac and Respiratory System Toxins
Round up of other common toxins including those affecting the hepatic system, cardiovascular and respiratory systems and other miscellaneous agents. We will look at identifying these patients as well as common sources of intoxication and approaches to management
Review of the process of gastric lavage and contraindications associated with this method of contamination
Specific concerns associated with other toxins, including xylitol, baclofen, beta blockers, paracetamol, garlic and onions
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Discuss appropriate treatment options and interventions for the mentioned toxins
Confidently provide nursing care and monitoring for these patients
Discuss gastric lavage and when it may not be appropriate
Appreciate the long term effects these toxins may or may not have on our patients
This course will be fully tutored by Kath Howie and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
September 9 (Monday) – October 4 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Kath HowieVTS (ECC), RVN Principal Nurse Manager, Vets Now

Course Details
Week 1 Diabetes Mellitus In this first week, we will be looking at diabetic cats and dogs and how nutrition plays a very large role in stabilisation
Course Details
Week 1
Diabetes Mellitus
In this first week, we will be looking at diabetic cats and dogs and how nutrition plays a very large role in stabilisation of blood glucose. In dogs, we will look at how manipulation of different types of fibre can influence it. Cats are completely different when it comes to diabetes, not just in what to feed them. We will look at low carbohydrate, higher fat and protein diets, and how these can be used for obesity control and aid with the diabetes
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand how diets for dogs and cats differ for diabetic patients
Explain how specific nutrients affect metabolism and insulin requirements
Establish safe weight loss in the diabetic cat
Week 2
Cardiac Disease
In the second week, we will look at the ACVIM consensus statement and how we can build this into nutrition for dogs. We will look at the recent evidence for cardiac diets and how the heart cells have been shown to respond to different energy sources. We will also look at the evidence surrounding those dogs that are developing DCM on grain free diets
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the nutritional requirements for the cardiac patient
Describe how to prevent cardiac cachexia
Understand the issues with fad diets and DCM
Week 3
Hepatic Disease
Hepatic disease in cats and dogs can be very complex depending on the cause. We will look at the feeding of puppies with portosystemic shunts and why we use diets with specific nutrients. We will then discuss those animals with raised liver parameters and how we can help them, using diets and supplements
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand how certain nutrients can exacerbate the clinical signs of portosystemic shunts
Explain how supplements can be used in animals with liver disease
Describe the nutrient requirements of cats and dogs with liver disease
Week 4
Dermatological Diets
In this last week, we will look at all the different diets that are available for dogs and cats that have dermatological issues. We will investigate nutrigenomic diets, novel protein diets and hydrolysed diets and discuss when to use each one
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the difference between diets aimed at animals with dermatological issues
Conduct feeding trials for dermatological cases
Explain how supplements can be used to improve skin conditions
The course will be fully tutored by Nicola Lakeman, and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
September 16 (Monday) – October 11 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Nicola LakemanMSc, BSc(Hons), RVN, CertVNECC, CertSAN, VTS(Nutrition) Nutrition Manager, IVC Evidensia
Course Details
Week 1 Triage Assessment and Stabilisation Carrying out an effective triage assessment and the RVN’s role Major body system assessment Approach to dysfunction of the cardiovascular, respiratory and neurological systems Practical considerations
Course Details
Week 1
Triage Assessment and Stabilisation
Carrying out an effective triage assessment and the RVN’s role
Major body system assessment
Approach to dysfunction of the cardiovascular, respiratory and neurological systems
Practical considerations for managing the emergency patient stabilisation
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Correctly identify a patient with dysfunction of a major body system
Confidently triage and assess an emergency patient
Recognise the approach to dysfunction of different major body systems and stabilisation techniques utilised for emergency patients
Appreciate specific nursing considerations for the emergency presentation
Week 2
Urethral Obstruction
Identification of the patient with urethral obstruction
Stabilisation techniques
Evidence-based discussion on emergency management, fluid types and analgesia options
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Participate in case based discussions
Identify the patient’s condition and the pathophysiology alongside potential complicating factors such as co-morbidities
Understand how to correct fluid deficits and identifying the difference between hypovolemia and dehydration
Participate in acid-base and electrolyte discussions, including how to address hypo and hyperkalemia
Appreciate the specific nursing considerations for patients with urethral obstruction
Week 3
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Presentation and initial emergency management
Acid base balance and electrolyte abnormalities
Pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis and complicating factors
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Participate in case based discussions
Identify the patient’s condition and the pathophysiology alongside potential complicating factors such as co-morbidities
Understand how to correct fluid deficits and identifying the difference between hypovolemia and dehydration
Participate in acid-base and electrolyte discussions, including how to address hypo and hyperkalaemia
Appreciate the specific nursing considerations for patients with DKA
Week 4
The Acute Abdomen – Surgical Cases
Pre-anaesthesia stabilisation and assessment
Analgesia choices in the critically ill patient
Peri-operative and recovery periods
Nursing specific concerns post operatively
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Develop a pre-anesthetic plan and discuss suitable stabilisation as well as attribute an ASA score
Complete with confidence a surgical checklist and identify areas of concern
Understand analgesia choices, the options we have including CRIS, local and regional techniques
Engage in cased based presentations, including abdominal foreign bodies and gastric dilatation and volvulus
Week 5
The Acute Abdomen – Medical Cases
Analgesia and pain scoring
Non-surgical versus surgical patients
SIRS and DIC
Nutritional support
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand pain scoring and the importance of using validated methods
Understand analgesia choices, the options we have including CRIS, local and regional techniques
Decide if a patient is surgical or non-surgical, especially in the case of traumatic haemoabdomen
Understand the pathophysiology behind systemic inflammatory response syndromes and disseminated intravascular coagulation and how to identify the early indications of development of these syndromes
Week 6
Acute Gastrointestinal Disease
Haemorrhagic gastroenteritis including parvovirus
Fluid therapy
Antibiosis
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify appropriate approaches to fluid replacement including discussion of the use of crystalloids and colloids in the patient with AHDS
Appreciate the importance of nutrition in the patient with acute gastro-intestinal disease and how we can provide that
Describe potential complications that may occur, including sepsis
Discuss the rational use of antibiotics, using evidence bases
The course will be fully tutored by Kath Howie and will consist of 15 hours of CPD and will be provided in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case scenarios, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
September 16 (Monday) – October 25 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Kath HowieVTS (ECC), RVN Principal Nurse Manager, Vets Now

Course Details
Week 1 Making Rabbit Anaesthesia Safer Pre-op advice for clients ASA grading – what increases the risk? Monitoring under general anaesthesia Post-operative care Learning objectives After completion of this week,
Course Details
Week 1
Making Rabbit Anaesthesia Safer
Pre-op advice for clients
ASA grading – what increases the risk?
Monitoring under general anaesthesia
Post-operative care
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Recap rabbit anaesthesia and how you can help build up your confidence, including pre op, intra op and post op care
Identify signs to be monitoring under anaesthesia – including CO2, SPO2, reflexes, HR, RR and BP readings
Use the ASA grading system, to look at why rabbits may be at a higher risk, compared with dogs and cats when placed under GA
Understand the options for intubation and maintaining an airway
Week 2
Analgesia – Taking the Pain Away
The signs of pain
Causes of pain
Knock on effects of uncontrolled pain
Analgesia options
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify the signs that rabbits show when in pain – these can be easily missed!
Learn how to use with the ‘Rabbit Grimace Scale’ in conjunction with clinical signs
Appreciate the secondary problems that pain can lead to, when it is not managed correctly
Know what analgesia options can be used in rabbits
Week 3
Preparing for an Emergency
Preparation at the practice
Triaging rabbits
Obtaining a capsule history
Assessment
Managing owner expectations
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Appreciate that when the phone rings it is important to be prepared for the emergency rabbit case. Know what to do and what equipment to set up to be ready
Understand how to triage rabbits and when continuing to do so may be detrimental
Obtain a quick and useful history from the owner to enable treatment to commence
Conduct a full assessment of the rabbit – from head to toe
Communicate with clients, managing their expectations and keeping them informed
Week 4
Critical Care – Keeping them Alive!
What is and what isn’t an emergency
What to do when faced with a rabbit emergency
Stabilisation and oxygen therapy
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify rabbit emergencies – they are not always obvious, and knowing what is and what isn’t an emergency is important
Understand the health conditions which are emergencies in rabbits, including gastrointestinal stasis/blockages, flystrike, liver lobe torsion and respiratory distress
Achieve the important goal of keeping stress to a minimum
Identify the signs of improvement and deterioration
The course will be fully tutored by Claire Speight and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
September 30 (Monday) – October 25 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Claire SpeightA1 Clinical Coach, C&G Cert Nursing Exotic Species, RVN Senior Nurse, Kettering Vets4Pets
Course Details
This four week course is designed to be a refresher in routine anaesthesia, and will cover the most up-to-date and relevant information. This course may be most beneficial
Course Details
This four week course is designed to be a refresher in routine anaesthesia, and will cover the most up-to-date and relevant information. This course may be most beneficial for nurses returning to work following a career break, or for nurses working in a different field (for example specialist medicine nurses) wishing to keep their anaesthesia knowledge refreshed and updated
Week 1
Preparation and Premedication
Preparing for what may happen is the key to anaesthesia. We will discuss how to approach an anaesthetic and the difference premedication can have on the patient and the anaesthetic that follows.
Preparedness
Considerations
Safe and effective premedication
Calculations for anaesthesia
Fasting periods
Medication that may be given prior to the visit
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List generalised considerations for preparing to anaesthetise routine cases
Confidently provide premedication prior to anaesthesia in a safe and controlled manner
Give advice on how long to withhold food before anaesthesia for a variety of different patients
Week 2
Induction
This week will cover the induction process, how to manage different case scenarios and guide you through intubation techniques.
Selection of an appropriate breathing system
Preoxygenation
Intubation for different cases
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Select an appropriate breathing system and calculate the fresh gas flow required
Understand the physiology of preoxygenation, and how to do this effectively
Confidently approach intubation in both routine cases and those with anatomical variations
Week 3
Maintenance
For many, the maintenance phase of anaesthesia can be daunting, this week we will discuss monitoring and fluid therapy during anaesthesia.
Multiparameter monitors
Hypotension
Fluid therapy during anaesthesia
Low flow anaesthesia
Environmental considerations
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Feel confident using multiparameter monitors and interpret the information given
Appreciate the physiology of and importance of monitoring blood pressure effectively
Select an appropriate fluid rate during anaesthesia Select an appropriate fresh gas flow rate during maintenance of anaesthesia
Recognise some of the environmental impacts of anaesthesia
Week 4
Recovery
The recovery phase is an area with high mortality in small animal patients, this week will cover how to make this phase of anaesthesia both calm and safe.
Practicalities of recovery
Monitoring post-anaesthetic
Pain scoring
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understanding the risks associated with and the necessity for monitoring patients in recovery
Confidently perform pain scoring assessments on patients following surgery
This course will be fully tutored by Will McFadzean and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
September 30 (Monday) – October 25 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
William McFadzeanBVetMed, CertAVP (VA), DipECVAA, MRCVS Cave Veterinary Specialists

Course Details
Week 1 Common Respiratory Disease Lower respiratory tract disease Pleural disorders Pulmonary disease POCUS and sampling Management Learning objectives After completion of this week, participants should be able to: Describe lower respiratory
Course Details
Week 1
Common Respiratory Disease
Lower respiratory tract disease
Pleural disorders
Pulmonary disease
POCUS and sampling
Management
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe lower respiratory tract physiology and the disease processes seen in practice
Understand the different causes of pleural disorders
Understand the different causes of pulmonary disease
Identify the uses of POCUS and understand which patients may benefit from thoracocentesis
Describe how to manage the patient with acute respiratory distress
Week 2
Oxygen Therapy
How to identify a patient in need of oxygen therapy
Non-invasive methods of oxygen therapy
Invasive methods of oxygen therapy
Monitoring a response to therapy
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand which parameters are used to identify patients are in need of oxygen therapy
Describe which methods of non-invasive oxygen therapy are available and which is the most suitable for their patient
Describe which methods of invasive oxygen therapy are available and which is the most suitable for their patient
Discuss whether a patient is responding to oxygen therapy and when a decision may be made to discontinue oxygen support
Week 3
Blood Gases
Why do we use blood gas analysis?
How to take a sample for a blood gas analysis
What is Acid/Base?
Interpretation of a blood gas report
Compensation
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand why blood gas analysis is important for managing the respiratory patient
Describe how to take a sample for blood gas analysis
Understand Acid/Base status and what this means for the patient
Interpret a blood gas report using a step by step approach so that this can be transferred to your patients in practice
Understand the physiology behind compensatory mechanisms
Week 4
BOAS – From Admit to Discharge
Admit considerations
BOAS Plan
Anaesthesia considerations
Dealing with the BOAS crisis
Other nursing considerations
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List the considerations which should be discussed with the owner when the patient is admitted to the hospital
Discuss safe ways of managing these cases whilst they are hospitalised to minimise complications
Understand how to make BOAS patients anaesthesia plans safer
Explain the concerns associated with a BOAS crisis and how to manage these
Describe other nursing considerations associated with these breeds and how we can factor these into our nursing care plans for hospitalised patients
Time
September 30 (Monday) – October 25 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speakers for this event
-
Elle Haskey
Elle Haskey
BSc(hons), VTS(ECC) VPAC A1, RVN
HEAD EMERGENCY AND CRITICAL CARE NURSE, ROYAL VETERINARY COLLEGE
BSc(hons), VTS(ECC) VPAC A1, RVN
-
Katie Gray
Katie Gray
Dip AVN, RVN
SENIOR EMERGENCY AND CRITICAL CARE NURSE, ROYAL VETERINARY COLLEGE
Dip AVN, RVN

Course Details
Veterinary nurses will likely have to nurse patients with varying degrees of neurological disease throughout their career. Understanding how a patient is affected neurologically, and knowing their basic
Course Details
Veterinary nurses will likely have to nurse patients with varying degrees of neurological disease throughout their career. Understanding how a patient is affected neurologically, and knowing their basic care needs, will allow for successful nursing of these patients in practice.
Although neurological patients may seem daunting initially, by going through these patients step-by-step from history, through diagnosis, treatment and nursing care, we can make these cases less daunting and more rewarding.
Each week we will look at a different aspect of veterinary neurology so that you gain a full picture of how and why certain treatment options are preformed/required. Following the course, you can apply the knowledge of various conditions and how these will affect the nursing care requirements of the patient, to produce successful nursing care plans, as well as fully support your clients that have pets with on-going neurological needs at home.
Week 1
Patient History and Assessment
Taking a thorough history
Initial patient assessment
Anatomy
Neurological examination
Localisation
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Successfully take a detailed history from owners and distinguish if the problem is neurological or not
Assess / triage the patient’s overall condition
Understand the neurological examination and describe what the findings may suggest
Discuss neurological lesion localisation and appreciate how this will allow planning of diagnostics tests
Week 2
Diagnostics
What do we need to know and when?
Blood tests
Urine
Imaging
MRI
CT
Radiography
Myelography
Ultrasound
Electrodiagnostics
Muscle and nerve biopsies
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand if diagnostic tests are required
Know what tests should be prioritised – especially in emergency / critical cases or money sensitive situations
Understand what genetic tests are routinely carried out in neurology
Have a basic understanding of advanced imaging protocols and which ones should be used
Understand why and when electrodiagnostics are used in practice
Discuss why muscle and nerve biopsies may be taken
Week 3
Spinal Conditions
Intervertebral disc disease and other common spinal conditions
Medical versus surgical treatment
Hemilaminectomy surgery, ventral slot surgery and other surgical approaches
Fenestration and durotomy – what does it mean and why?
Atlanto-axial instability, fractures and other vertebral malformations
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Display knowledge about common spinal conditions seen in practice and understands why surgery is or isn’t performed
Describe how surgery affects the patient’s anatomy. Understanding surgery allows for a more considerate approach to nursing these patients
Show an awareness of any likelihood of recurrence
Week 4
Brain Disease
Seizures
Meningoencephalitis of unknown origin (MUO)
Vestibular disease
Head trauma
Neoplasia
Toxins
Otitis media / interna
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Explain primary and secondary seizures and potential causes, and understand when to start anti-epileptic treatment
Discuss the clinical signs of MUO, how it is diagnosed in practice, along with the treatment options available
Know how to triage the emergency head trauma patient and use the Glasgow Coma Scale
List other causes of disease that may cause patients to present similarly to brain disease patients
Week 5
Neuromuscular Disease
Common neuromuscular diseases seen in the UK
Myasthenia Gravis
Polyradiculoneuritis
Tetanus
Toxoplasmosis
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Show an understanding as to how different neuromuscular diseases affect our patients
Discuss treatment options available to patients for these conditions and know the nursing care required to support them during their recovery
Week 6
Nursing the Neurological Patient
Nursing care required to successfully nurse patients in hospital
Bladder dysfunction and care
Nutritional / hydration needs
Handling techniques
Exercise
Complications
Complementary treatment options
Promoting good overall patient care in practice
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Consolidate knowledge from the whole course to successfully produce nursing care plans for a variety of neurological conditions
Identify which bladder management technique is required for various patients
Understand appropriate handling techniques and when one should be used over another
Help support clients that have pets with ongoing neurological care needs at home
Discuss the long-term care and monitoring these patients may require
This course will be fully tutored by Zoe Hatfield and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
September 30 (Monday) – November 8 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Zoe HatfieldVTS (IM-Neurology), RVN Neurology Nurse, Glasgow Vet School
Course Details
Week 1 Principles of Anaesthetising Critical Patients Anaesthetic risk in the compromised patient The importance of patient history and physical examination Diagnostic tests Patient stabilisation Anaesthetic protocol, monitoring and recovery Learning objectives
Course Details
Week 1
Principles of Anaesthetising Critical Patients
Anaesthetic risk in the compromised patient
The importance of patient history and physical examination
Diagnostic tests
Patient stabilisation
Anaesthetic protocol, monitoring and recovery
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand why critical patients are at an increased anaesthesia and sedation risk
Understand that improving patient safety requires a holistic, overall management process, not simply using “the best drug protocol”. This will include consideration of:
What pre-anaesthetic tests may be required and the benefit they offer
What pre-anaesthetic stabilisation may be required
Recall an introduction into the type of patient monitoring which is required during the peri-anaesthetic period
Understand general principles for appropriate anaesthetic drug protocols for the critical patient
Week 2
General Approach to Adverse Events and Introduction to Anaesthetic Complications
Near misses and adverse events
Minimising adverse events by preparation
Checklists and non-technical skills
Common anaesthetic complications
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Name the three steps necessary for approaching adverse events and discuss why they are important, including methods in which near misses and adverse events can be minimised in practice
Understand the role of human factors in patient safety and the value of checklist use in anaesthetic practice
Give an overview of what anaesthetist non-technical skills (ANTS) are and be able to begin using them in clinical practice
Know the most common anaesthetic complications encountered in small animal practice
Week 3
Cardiovascular Complications
Alterations in heart rate:
Bradyarrhythmias
Tachyarrhythmias
Alterations in blood pressure:
Hypotension
Hypertension
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Recognise abnormal physiological parameters with regards to the cardiovascular system for individual patients undergoing anaesthesia
Understand the most common underlying causes for alterations in heart rate (bradyarrhythmias and tachyarrhythmias) during general anaesthesia
List some main treatments for the most common arrhythmias which present under general anaesthesia
Understand the most common underlying causes for alterations in blood pressure (hypotension and hypertension) during general anaesthesia
List some main treatments for the most common blood pressure alterations which present under general anaesthesia
Begin to apply this knowledge to individual cases within the clinic with use of the available equipment
Week 4
Respiratory Complications
Alterations in ventilation:
Hypoventilation
Hyperventilation (including tachypnoea)
Apnoea or respiratory arrest
Hypoxaemia
Respiratory obstruction:
Upper respiratory tract
Lower respiratory tract
Restrictive pulmonary disease
Aspiration (and regurgitation)
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Recognise what are abnormal physiological parameters with regards to the respiratory system for individual patients undergoing anaesthesia
Understand the most common underlying causes for alterations in ventilation, including hypo- and hyperventilation, apnoea and respiratory arrest
List the main treatments for the most common changes in ventilation under anaesthesia.
Understand the difference between hypoxaemia and hypoxia, listing the potential causes for these and therefore be able to suggest methods to manage these conditions
Recognise the clinical signs of respiratory obstruction and restrictive pulmonary disease and describe what steps could be taken to alleviate the underlying problem
State why aspiration is a risk under anaesthesia and how to manage a case of gastro-oesophageal reflux in order to minimise patient risk
Begin to apply this knowledge to individual cases within the clinic with use of the available equipment
Week 5
‘Other’ Complications
Central nervous system:
Emergence delirium
Post anaesthetic blindness and deafness
Thermoregulation:
Hypothermia
Hyperthermia
Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions
Embolism
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Outline why cats are at particular risk for post anaesthetic blindness and deafness and describe methods which can minimise this risk
List available methods for patient warming, with recognition of the need to counteract patient hypothermia and the potential risks associated with warming device use
List risk factors associated with peri-operative hyperthermia and discuss steps which can be implemented to manage the hyperthermic patient
Recognise if an anaphylactic or anaphylactoid reaction is occurring and be able to suggest steps to manage the situation
Understand that embolisms are a rare, but potential complication during anaesthesia and be able to list the clinical signs associated with their occurrence
Week 6
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Detecting cardiopulmonary arrest
Basic life support:
Chest compressions
Tracheal intubation
Ventilation
Advanced life support
Drug therapy
Oxygen supplementation
Intravenous fluid therapy
Correction of electrolyte and metabolic disturbances
Defibrillation
Monitoring during CPR
Post cardiac arrest care
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Explain the purpose of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and describe its two main components
Recognise when cardiopulmonary resuscitation should be instigated
Understand the importance of regular CPR training within the practice team
Describe and demonstrate the method for effective chest compressions, tracheal intubation and ventilation during cardiopulmonary resuscitation
List what steps can be taken to provide advanced life support during cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Know what monitoring tools are recommended for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and be able to interpret the main waveforms that will be seen during a resuscitation event
This course will be fully tutored by Becky Robinson, and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
September 30 (Monday) – November 8 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Rebecca RobinsonBVSc, MVetMed, DipECVAA, FHEA, MRCVS EUROPEAN & RCVS SPECIALIST IN VETERINARY ANAESTHESIA, DAVIES VETERINARY SPECIALISTS
october 2024

Course Details
The aim of this course is to introduce veterinary nurses to exotics in practice. The emphasis will be placed on examination and handling techniques as well as essentials
Course Details
The aim of this course is to introduce veterinary nurses to exotics in practice. The emphasis will be placed on examination and handling techniques as well as essentials of anaesthesia, imaging techniques, and making the veterinary visit as stress-free as possible for pets. This will enable exotics and small mammals to be incorporated into any small animal practice with standard facilities.
Week 1
The Rabbit Consultation
Handling, examination and history taking
Preventative care
Making your clinic rabbit friendly
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Appreciate the importance of stress reduction in rabbits, including during hospitalisation and examination
Understand essentials of preventive care of rabbits
Understand handling and therapeutic techniques in rabbits
Week 2
Anaesthesia of Small Furries
Basic anaesthesia
Reducing stress around anaesthesia
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe a holistic approach to stress reduction in the peri-anaesthetic period to improve anaesthetic success rates
Prepare a patient for anaesthesia
Understand how to provide airway support for rabbits
Week 3
Examination of Parrots
Handling and examination of parrots
Basic husbandry of parrots
Routine grooming techniques
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Achieve safe handling techniques for parrots
Understand the basic husbandry of pet parrots and how this relates to disease
Appreciate and apply the techniques of beak, nail and wing trimming and understand how issues with these adnexa may reflect systemic disease
Week 4
Avian Anaesthesia and Imaging
Basic anaesthesia techniques
Introduction to avian radiography and ultrasound
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Appreciate basic anaesthetic techniques, including induction and intubation, to improve anaesthetic success rates
Take a well-positioned radiograph and interpret the image
Understand the indications for ultrasonography in birds
Week 5
Reptile Examination Techniques
Handling
Examination techniques
History taking, including the husbandry review
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Achieve safe handling techniques of reptiles – snakes, lizards and chelonia
Perform a basic examination of these species
Appreciate the role of husbandry in reptile disease and how to conduct a full husbandry review
Week 6
Reptile Anaesthesia, Imaging and Hospitalisation
Basic anaesthesia techniques
Introduction to reptile radiography and ultrasound
Hospitalisation requirements for reptile species
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Appreciate basic anaesthetic techniques, including the importance of ventilation and when to use it
Take a well-positioned radiograph
Perform ultrasonography in reptiles
Understand the hospitalisation needs of reptile species
This course will be fully tutored by John Chitty and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
October 14 (Monday) – November 22 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
John ChittyBVetMed, Cert ZooMed, CBiol, MRSB, MRCVS RCVS ADVANCED PRACTITIONER IN ZOOLOGICAL MEDICINE, ANTON VETS

Course Details
In recent years there has been a marked interest in identifying the causes of gastrointestinal disease in companion animals; the path to diagnosis has progressed with the identification
Course Details
In recent years there has been a marked interest in identifying the causes of gastrointestinal disease in companion animals; the path to diagnosis has progressed with the identification of serological biomarkers and more access to endoscopy within general practice. Novel protein diets have been developed by veterinary food companies resulting in a positive effect on outcome in combination with pharmaceuticals for some animals.
The veterinary nurse plays a key role investigation, treatment and client support for these often, chronic cases. Having an enhanced level of knowledge on the pathophysiology and treatment options, together with a firm understanding of the diagnostic process is paramount to patient recovery.
After completing this 6 week online course, the participants will have a greater knowledge and understanding of the basic principles of gastrointestinal disease which they can apply regularly in practice.
Week 1
Diseases of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
Upper gastrointestinal tract (UGIT) anatomy refresher
UGIT hereditary and acquired abnormalities
Investigation of vomiting and regurgitation
Sedation and general anaesthesia considerations
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List the main structures of the UGIT
Describe the normal function and processes of the UGIT
Identify the difference between vomiting and regurgitation and the common causes
Understand the diagnostic approach to patients with UGIT symptoms
Explain the reasons why patients with UGIT disease are higher risk for investigative procedures
Evaluate current methods used in practice to sedate patients with UGIT disease and analyse if modifications to practice would be beneficial
Week 2
Diseases of the Lower Gastrointestinal Tract
Lower gastrointestinal tract (LGIT) anatomy refresher
LGIT pathophysiology
Mechanisms and classification of diarrhoea
Investigative process for LGIT symptoms
Patient preparation for GI endoscopy
Supportive treatment for patients with LGIT
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List the main structures of the LGIT
Describe the normal function and processes of the LGIT
Differentiate diarrhoea types and common causes
Understand the diagnostic approach to patients with LGIT symptoms
Evaluate current care plans used in practice to prepare patients for endoscopy and analyse if modifications to practice would be beneficial
Summarise the key therapeutic treatments for patients with LGIT
Week 3
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Anatomy and functions of the gastroscope
Cleaning and sterilising procedures
Endoscopy sourcing, storage, and auditing
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Label the main components and list the functions of a gastroscope
Explain the bedside procedure for cleaning and then sterilising the gastroscope
Select the correct biopsy tools and materials for optimal sampling and histological value
Evaluate practice protocols to standardise in line with current best practice
Week 4
Interventional Endoscopy
Foreign body removal
Balloon dilatation
Injection of steroids and anti-inflammatory medications
Endoscopically placed feeding tubes
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List the various interventional uses of gastrointestinal endoscopy
Select the correct forcep tool for foreign body retrieval
Describe the ballooning technique use for oesophageal strictures
Explain the indications, risks and technique for placing a PEG tube
Week 5
Nursing Patients with Gastrointestinal Disease
Nursing basics and care plans
Pain and emesis management
Oesophageal tube placement
Assisted feeding methods
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List the essential care requirements for nursing patients with GI disease
Identify symptoms of pain and nausea
Compare patient assessment tools to monitor status and benchmark interventional treatment
Calculate energy requirements and feeding volumes for tube feeds
Week 6
Enteropathy Therapeutics and Nutrition
Terminology of diseases
Pathways and mechanisms of enteropathies
Medications and therapies
EBVM current information
Dietary needs
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Differentiate between terms associated with chronic enteropathies
Analyse the treatments allocated to different types of enteropathy
Refer to updated resources and guidelines to further inform their knowledge and subsequently refer to it at a later date
Explain what a diet trial is
List the types of dietary allergen there are
The course will be fully tutored by Nicola Read and Gina Parkes and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case scenarios, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
October 21 (Monday) – November 29 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speakers for this event
-
Gina Parkes
Gina Parkes
DipAVN(Small Animal), AFHEA, RVN
DipAVN(Small Animal), AFHEA, RVN
-
Nicola Read
Nicola Read
PgC (Oncology Veterinary Nursing), DipAVN (Med), RVN
Nicola qualified in 2000 from a well established small animal general practice in North West London where she also gained the D32/33 Assessor qualification. She spent a year at Battersea Dogs and Cats Home in 2001 to gain experience in a charity based organisation and then moved to the Queen Mother Hospital, Royal Veterinary College in 2002, in order to study for the RCVS advanced diploma. In June 2008 she became the Head Medicine Nurse at the Royal Veterinary College and is currently working towards the American Internal Medicine Veterinary Technicians Certificate. Her clinical interests are endocrinology, gastroenterology, oncology and immune-mediated disease.
PgC (Oncology Veterinary Nursing), DipAV…
Course Details
Week 1 Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Traumatic brain injury is a relatively common emergency presentation following road traffic accidents or other traumatic episodes. There are several priorities
Course Details
Week 1
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Traumatic brain injury is a relatively common emergency presentation following road traffic accidents or other traumatic episodes. There are several priorities to consider when nursing these patients, which are vital to support their recovery. We will discuss the initial approach to these patients including the use of mannitol and hypertonic saline, along with analgesia and specific nursing techniques that minimise intra-cranial pressure. Use of the Glasgow Coma Scale is very helpful in these patients and should be part of our toolbox. Ongoing patient care beyond the first 24 hours will be discussed, including options for nutritional support and continued management.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Determine the difference between a patient with TBI compared to those with facial trauma or altered mentation for another reason
Understand the difference between primary and secondary brain injury
Appreciate the interventions that will make these patients worse and how to mitigate that risk
Confidently conduct a neurological assessment to complete the Glasgow Coma Scale assessment
Understand the ongoing problems these patients may encounter and how to resolve them
Week 2
Heat Stroke
Despite several media campaigns, we continue to see patients presenting with heat stroke every year. The nursing team are vital to the recovery and ongoing management of these patients and rapid recognition at triage can lead to improved outcomes. We will look at methods for cooling these patients, the issues we may encounter with them on presentation but also the potential for complications such as Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) and Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC).
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Determine the difference between heat stroke, heat stress and pyrexia
Understand the priorities for treatment of these patients
Discuss effective cooling methods by reviewing the evidence bases available
Understand the complications associated with heat stroke including development of SIRS and DIC
Week 3
Common Intoxications
Intoxication is a common emergency presentation and the range of toxins our patients can encounter in the environment and the home is very variable. We will look at the toxins that are most encountered and how we need to approach and address these including nephrotoxins and CNS toxins. We will look at treatment considerations including the use of intravenous lipid emulsion and the evidence supporting its use. Ongoing patient management and monitoring will be discussed in detail.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the approach to the intoxicated patient and our priorities
Explain how intravenous lipid emulsion works and which patients it may be suitable for
Provide nursing care for the patient requiring prolonged sedation or anaesthesia due to intoxication
Effectively monitor the patient depending upon the toxin that has been ingested
Week 4
BOAS Crisis
We see an increasing number of brachycephalic patients presenting in respiratory distress. It is vital we are confident at managing these patients from initial admission to stabilisation and ongoing management. We will discuss the anatomy that leads to airway obstruction and the priorities when we are faced with a patient in a BOAS crisis. When to anaesthetise and intubate is a vital consideration as well as when we might consider placing a tracheostomy tube.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the conformation issues and environmental factors that may lead to a BOAS crisis
Identify other complications associated with the syndrome and explain how to manage them, including regurgitation and hiatal hernia
Confidently manage a tracheostomy tube patient and understand the indications for placement
The course will be fully tutored by Kath Howie and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
October 28 (Monday) – November 22 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Kath HowieVTS (ECC), RVN Principal Nurse Manager, Vets Now
november 2024

Course Details
Week 1 Preparing to Feed Patients within the Veterinary Hospital This week aims to identify the key pieces of information required from the pet owner, in order to
Course Details
Week 1
Preparing to Feed Patients within the Veterinary Hospital
This week aims to identify the key pieces of information required from the pet owner, in order to give their pets the best chance of voluntarily consuming food whilst in the veterinary hospital.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify which information is vital to collect from the pet owner
Appreciate the who, how and when of information collection
Understand how to create the ideal eating environment for your patients
Understand all aspects of the hospital food kitchen
Week 2
Hospital Nutrition
Every effort should be made to get patients eating on their own. Choosing appropriate foods and timings will largely depend on the results of the nutritional assessment. Patients may not eat well whilst they are in the hospital, for a wide range of reasons, and nutritional support may be required; firstly we tempt them to eat and if unsuccessful, look at other methods of assisted feeding.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand how to feed appetent patients:
Communicate the nutrition plan
Select appropriate foods and feeding times
Offer a tailored approach to each individual patient
Understand how to feed inappetent patients:
Appreciate the available options
Identify environmental adaptations
Offer assisted feeding
Week 3
Critical Care Nutrition
Despite all efforts some patients may be either too unwell or unwilling to voluntarily consume any food whilst in the hospital, and assistance in the form of feeding tubes will be required.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the process of feeding tube selection
Provide maintenance and care of feeding tubes
Confidently calculate nutritional requirements and food quantities
Week 4
Diabetic Patients
A diagnosis of diabetes can be very worrying and overwhelming for pet owners with many elements to consider. Nutrition plays a vital role in the management of both cats and dogs with diabetes. As the type of diabetes frequently seen in dogs and cats differ, a disease specific recommendation will be required.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Implement stable feeding routines for diabetic dogs
Describe the ideal food composition for diabetic cats
Understand how to manage concurrent obesity
Week 5
Multiple Concurrent Conditions and Difficult Decisions
As with many things in life, challenges rarely occur alone. Patients often present us with dietary dilemmas and decision making can be difficult. However, by knowing what to prioritise, where to compromise and where to go for help, a suitable nutritional solution can be found for all.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Explain nutritional care for end of life patients
Provide nutritional advice for patients with concurrent diseases
Understand what to do when no suitable diet exists
List sources of additional nutritional information
Week 6
Client Communication
Although much in known about providing nutrition in many different circumstances, excellent client communication is a key part of dietary plan implementation. Getting communication right means your recommendation is more likely to be followed, clients know who to trust and who they should talk to if problems arise. This is an excellent way to demonstrate the high level of care you are providing to their beloved pet.
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Create the right environment for discussions
Gauge readiness of the client to discuss their pet’s diet
Approach information gathering to maximise responses
Understand what to do if the owner is feeding a nonstandard diet
Make clear recommendations and manage expectations
Monitor and make adjustments to the nutrition plan
This course will be fully tutored by Georgia Woods-Lee and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
November 4 (Monday) – December 13 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Georgia Woods-LeeBSc(Hons), RVN, Cert CFVHNut, VTS (Nutrition) WEIGHT MANAGEMENT CLINIC NURSE, UNIVERSITY OF LIVERPOOL

Course Details
Week 1 The Nurse’s Role in Medical Clinics – When, Why and How? Why set up a monitoring clinic? How to set up a monitoring clinic Equipment needed for a monitoring
Course Details
Week 1
The Nurse’s Role in Medical Clinics – When, Why and How?
Why set up a monitoring clinic?
How to set up a monitoring clinic
Equipment needed for a monitoring clinic
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the importance of nurses being involved in the long term monitoring of cats with medical diseases
Visualise how they would be able to set up this type of clinic in their own practice
Feel ready to learn and revise common chronic feline disease and become up to date with the latest evidence
Week 2
Managing Chronic Kidney Disease
What is CKD?
What effects does CKD have on the body?
How to monitor CKD
Treatment aims for CKD
IRIS staging
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the pathophysiology of CKD
Identify parameters used to monitor the CKD patient
Understand the IRIS staging scheme
Understand what treatments are appropriate at which stage of disease
Use evidence based medicine to help educate your clients
Week 3
Managing Diabetes Mellitus
What is diabetes mellitus?
How to monitor diabetes mellitus
Treatment aims for diabetes mellitus
Owner support for cats with diabetes mellitus
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus
Understand the difference between cats and dogs with diabetes mellitus
Understand how to monitor diabetes mellitus and the importance of blood glucose curves
Understand what treatments are available for diabetes mellitus
Counsel owners of cats with diabetes mellitus
Week 4
Managing Degenerative Joint Disease
How prevalent is DJD in cats?
How to assess cats for DJD
Treatments for DJD
How to engage owners in the treatment and monitoring of DJD
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the prevalence of DJD in cats and use that information in the nursing treatment and handling of the cat
Assess cats using a variety of methods both in the clinic and at home for DJD
Understand the different treatments available for DJD
Educate owners about the treatments and how the owner can assess the cat to
improve compliance
The course will be fully tutored by Suzanne Rudd and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
November 11 (Monday) – December 6 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Suzanne RuddDipAVN(Medical) RVN The Feline Centre, University of Bristol
january 2025

Course Details
Week 1 Recumbency Nursing Common causes for recumbency Nursing the recumbent patient Common complications associated with recumbency Learning objectives After completion of this week, participants should be able to: List
Course Details
Week 1
Recumbency Nursing
Common causes for recumbency
Nursing the recumbent patient
Common complications associated with recumbency
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List some of the common causes for recumbency and how these conditions may be treated
Discuss the nursing considerations for the recumbent patient and how these can be implemented to help support the patient during their recovery whilst hospitalised
Describe the common complications associated with recumbency and how these can be prevented whilst the patient is hospitalised
Week 2
Nutrition in the Hospitalised Patient
Why is nutrition important?
Who needs nutrition?
When should nutrition be started?
Creating a nutrition plan
Assisted feeding options
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand why nutrition is important for the recovery of hospitalised patients
Identify patients in needs of nutrition
Discuss when is the appropriate time to start nutrition in their hospitalised patient
Describe how to create a feeding plan including patient assessment, calculation of RER and implementation of the nutritional plan
List the common assisted feeding techniques and understand the indications and contraindications of each
Week 3
Sepsis
What is SIRS / sepsis?
How to recognise sepsis in dogs
How to recognise sepsis in cats
Sepsis bundles
Recent sepsis research in human medicine
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Know the definitions of SIRS / sepsis and the difference between them
List the patient observations used to help us be able to recognise sepsis in the dog
List the patient observations used to help us be able to recognise sepsis in the cat
Understand what a sepsis bundle is, and when they can be used in practice
Understand the recent research into sepsis in human medicine and how this impacts us in veterinary practice
Week 4
Acid Base / Electrolytes
What is acid / base?
What are electrolytes?
Electrolytes – Sodium
Electrolytes – Potassium
Electrolytes – Calcium
Glucose
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Explain acid / base status
Understand which electrolytes we can measure in veterinary practice and why
Identify when a patient may become hypo or hypernatraemic, and describe the treatments that may benefit them
Identify when a patient may become hypo or hyperkalaemic, and describe the treatments that may benefit them
Identify why a patient may be hypo or hypercalcaemic, and describe the treatments that may benefit them
Identify why a patient may be hypo or hyper glycaemic, and describe the treatments that may benefit them
Week 5
Infection Control
How to create an infection control plan for the clinic
Assigning an infection control champion
Identify and develop protocols
Make an assessment
Staff education and training plans
Surveillance and compliance
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify an infection control champion in practice and understand their role in the infection control plan
Discuss the common infection control protocols required in practice to minimise the spread of pathogens
Understand how to make an assessment of the protocols already in place and identify their strengths and weaknesses
Explain the importance of staff education and training when implementing infection control protocols
List the common surveillance techniques to ensure compliance to the infection control plan
Week 6
End of Life Care and Clinical Governance
Euthanasia
Palliative care
Mental health awareness
Clinical governance in practice
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the reasons vets and clients consider euthanasia, and learn ways to ensure the experience can be made as peaceful and calm as possible in practice for all involved
Understand the reasons that clients may choose to consider palliative care, and how we can help ensure the patients are comfortable within our role as veterinary nurses
Understand the impact of euthanasia and how the death of a pet can affect both the family of the patient and the veterinary staff involved
Understand the mental health implications of veterinary medicine on the team, and ways in which we can help our team and ourselves to cope
Describe what clinical governance is, what is discussed and why it may be beneficial to start holding these meetings in your practice
The course will be fully tutored by Elle Haskey and Katie Gray, and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case scenarios, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
January 6 (Monday) – February 14 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speakers for this event
-
Elle Haskey
Elle Haskey
BSc(hons), VTS(ECC) VPAC A1, RVN
HEAD EMERGENCY AND CRITICAL CARE NURSE, ROYAL VETERINARY COLLEGE
BSc(hons), VTS(ECC) VPAC A1, RVN
-
Katie Gray
Katie Gray
Dip AVN, RVN
SENIOR EMERGENCY AND CRITICAL CARE NURSE, ROYAL VETERINARY COLLEGE
Dip AVN, RVN

Course Details
This 6 week course will cover many different aspects of nursing orthopaedic patients in first opinion practice, and the role nurses can play in giving these patients the
Course Details
This 6 week course will cover many different aspects of nursing orthopaedic patients in first opinion practice, and the role nurses can play in giving these patients the best chance of an optimal recovery.
Week 1
The Orthopaedic Trauma Patient
Presentation
Triaging wounds
Initial wound management
Open fracture management
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Prepare equipment for initial stabilisation of the trauma patient
Select dressings and materials for initial wound management
Understand the grading system for open fractures and how this affects management of these cases
Prepare all necessary items for treatment of open fractures
Week 2
Preparing the Patient for Surgery
Clipping and preparing the patient
Orthopaedic theatre nursing
Theatre set up
Instrumentation
Scrub nurse role
Cleaning and sterilising
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Create an appropriate surgery schedule
Identify common orthopaedic surgical instruments and their use
Prepare and confidently check the theatre set up for a range of procedures, including equipment
Have a full understanding of orthopaedic equipment and how to care for it correctly
Understand the benefits a scrub nurse provides to the surgeon, the patient and the surgical procedure
Week 3
Orthopaedic Procedures – So Many to Choose From!
Surgery
Arthroscopy
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the options available for common orthopaedic conditions
Create a case study for a patient they have been involved in the nursing care of
Identify common surgical equipment, its use and how to prepare for surgery
Week 4
Fracture Repair – Internal Fixation
Fracture classification
Implants and consumables
Surgical instruments and equipment
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify common surgical implants used in fracture repair
Understand how the method of repair used will impact on the care required for the patient post-operatively
Week 5
Fracture Repair – External Fixation
Implants and consumables
Surgical instruments and equipment
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify common surgical implants used for external fracture repair
Understand the instructions required by owners for the ongoing care and management of patients with external fixators
Week 6
Recovery and the Post-Operative Period
Recovery from anaesthesia
Immediate therapy
Ongoing nursing care plans
Surgical complications
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Create nursing care plans for post-operative surgical patients
Develop the team role for nurses in the rehabilitation of orthopaedic patients
Understand the key responsibilities for client communication and post-operative care
Identify common complications and how to ensure owners understand the potential consequences
The course will be fully tutored by Alison Young and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
January 6 (Monday) – February 14 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Alison YoungDipAVN (Surgical), VTS (Surgery), RVN Head Theatre Nurse, Royal Veterinary College
Course Details
This 4 week tutored course will guide the candidates through the complexities of multiparameter monitoring. After completion of the course, candidates will better understand the effects of anaesthesia
Course Details
This 4 week tutored course will guide the candidates through the complexities of multiparameter monitoring. After completion of the course, candidates will better understand the effects of anaesthesia on the patient and causes of abnormalities encountered while monitoring anaesthetised patients. They will be able to use hands-on techniques and the multiparameter monitor to detect problems before they become serious, and to differentiate between artefacts and real patient issues to improve the safety of their patients.
Week 1
What are we Monitoring and Why?
What anaesthesia does to the patient and what we can do about it
Monitoring depth of anaesthesia
Temperature monitoring
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand why good monitoring is essential for safe anaesthesia
Understand the challenges of monitoring depth of anaesthesia
Appreciate the importance of monitoring body temperature and the consequences of hypo- and hyperthermia
Week 2
Monitoring the Respiratory System
Capnography
Pulse oximetry
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the physiology involved in the formation of the capnograph trace
Interpret normal and abnormal capnograph traces
Understand the physiology behind pulse oximetry, and its limitations
Confidently troubleshoot abnormal capnography traces and pulse-oximetry readings
Week 3
Monitoring the Cardiovascular System
Physiology of heart rate and blood pressure control
The electrocardiogram
Blood pressure monitoring
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the causes of heart rate and blood pressure changes during anaesthesia
Describe how the electrocardiogram is generated
Interpret the electrocardiogram
Understand the different techniques for measuring blood pressure
Interpret blood pressure readings and understand causes of inaccurate readings
Week 4
Monitoring with Blood Work and Troubleshooting Equipment
Blood gas and acid-base
Glucose monitoring and other tests
Monitor-related artefacts and technical problems
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand when blood gas analysis is useful
Interpret blood gas analyses in the light of the patient’s history and clinical problems
Decide when glucose monitoring and other tests during anaesthesia are important
Troubleshoot monitor-related issues
The course will be fully tutored by Colette Jolliffe, and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
January 13 (Monday) – February 7 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Colette JolliffeBVetMed, CertVA, DipECVAA, FRCVS European and RCVS Recognised Specialist in Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia, Anderson Moores Veterinary Specialists

Course Details
Week 1 From Conception to Weaning Parent health prior to conception and how this may affect pregnancy, parturition, and offspring Nutritional requirements during pregnancy Nutritional adaptations required during lactation Neonate nutritional requirements,
Course Details
Week 1
From Conception to Weaning
Parent health prior to conception and how this may affect pregnancy, parturition, and offspring
Nutritional requirements during pregnancy
Nutritional adaptations required during lactation
Neonate nutritional requirements, including how to hand feed effectively
Weaning
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Discuss how nutrition affects reproduction and key adaptations that are required
Have a clear understanding of how to promote health through nutrition during lactation
Identify the essential nutritional requirements for neonates
Understand how to hand feed neonates correctly
Week 2
Growth
Optimal growth
Effects of neutering
Nutritional considerations for large breed puppies
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Correctly use growth charts to map growth
Identify when growth is not ideal and the necessary changes that are required to maintain a healthy weight to adulthood
Have a good understanding of the nutritional adaptations that will be required at the point of neutering
Week 3
Adult Maintenance
Promoting health in adults
Maintaining a stable weight
Treat management
Recognise key aspects of feeding working dogs
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand nutritional requirements for adults and how these must be adapted for each pet’s circumstance
Identify points of concern and to make appropriate recommendations
Reflect on how nutritional requirement for working dog may differ from pet dogs
Week 4
Golden Oldies – Senior Pets
Defining ‘senior’ age as an individual process
Understanding age related changes and how these require nutritional adaptation
Environmental considerations for pets in their senior years
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Confidently assess the needs of a senior pet
Identify environmental changes that may be required
Understanding of the dynamic changes to nutrition that are required for seniors to better support the pet and pet owner
Week 5
Diet Choices
Examination of the pet food label
Introduction to alternative diet types and how to have conversations with pet owners
How to manage pets fed an alternative diet within a hospital environment
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify all key information on a pet food label and how this is used to determine a feeding amount
Have a broad understanding of the pros and cons associated with alternative diets that are now commonly fed
Appreciate methods for assessing the suitability of alternative diets and how to improve safety
Confidently talk to the pet owner who wish to feed an alternative diet type
Week 6
Maintaining an Ideal Weight
Assess ideal weight through body condition scoring and muscle condition scoring
Simple steps to ensure obesity does not occur, and what can help if it does
How to calculate a feeding quantity of dry, wet or mixed diet types
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Confidently be able to body condition score and muscle condition score to identify an ideal weight and good health
Understand how simple food management in the home can prevent obesity occurring
Thoroughly understand calculations for determining a feeding amount to prevent over, or under feeding
This course will be fully tutored by Georgia Woods-Lee and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
January 20 (Monday) – February 28 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Georgia Woods-LeeBSc(Hons), RVN, Cert CFVHNut, VTS (Nutrition) WEIGHT MANAGEMENT CLINIC NURSE, UNIVERSITY OF LIVERPOOL
february 2025
Course Details
As RVN’s we can be involved with assisting the surgery for dental treatments, but more often our role within the dentistry suite falls into the role of monitoring
Course Details
As RVN’s we can be involved with assisting the surgery for dental treatments, but more often our role within the dentistry suite falls into the role of monitoring and assisting with the anaesthesia plan for our dentistry procedures. This can be a daunting prospect with many factors to consider. This course will help reduce stress and increase confidence and positivity within the dental suite.
As RVN’s we are also in the perfect position to ensure a high standard of post operative care is provided to our patients, both within the hospital and when they are discharged into the care of their owners.
Week 1
Dentistry Analgesia
Different analgesia drugs available
Dose selection
Routes of administration
Drug combinations
Local nerve blocks
Sides effects of drugs
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Assist the veterinary surgeon in selecting appropriate analgesic drugs for different oral surgeries
Be aware of potential side effects of these drugs
Alongside the veterinary surgeon, create a tailored drug protocol for each patient to go home with
Comfortably calculate analgesic drugs at low doses
Be aware of what drugs are suitable as a combination
Understand the exclusion or reduced dose of some drugs, regarding co-morbidities
Use pain scoring methods and understand what analgesia the patient may need
Week 2
Anaesthesia – Airway Security and Hypothermia
How to maintain a patent airway
Patient positioning
To cuff or not to cuff?
Causes of hypothermia
Negative effects of hypothermia
Preventing and treating hypothermia
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand different styles of ET tubes and their benefits and potential negatives
Understand appropriate ET tube cuff pressures and why this is so integral to protecting the airway
Appreciate techniques to protect the airway
Know the gold standard method to move patients under anaesthesia, whilst protecting their airway
List the common causes of hypothermia
Understand the negative effects of hypothermia
Have practical knowledge on how to prevent and treat hypothermia
Understand the risk of using some heating devices
Week 3
Anaesthesia – Managing Hypotension
Causes of hypotension
Negative side effects of hypotension
How to obtain accurate blood pressure reading
How to prevent hypotension
Fluid therapy
Anaesthesia drug choices
The use of vasopressors and anticholinergics
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Obtain accurate blood pressure readings for cats and dogs under general anaesthesia for dentistry
Understand the limitations of blood pressure measurements and trouble shoot potential problems
Know what is deemed as an appropriate blood pressure reading under general anaesthetic
Know which drugs may interfere with maintaining blood pressure
Understand what could happen to our patients if left hypotensive
Feel more confident, alongside the veterinary surgeon, in making a treatment plan tailored to each individual patient, to treat any hypotensive episodes
Week 4
Post-operative Care
Immediate post op care once extubated
Care for patients in the recovery ward
Discharge instructions
Post op care at home
Post op checks
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Maintain and monitor a patent airway in the immediate post-operative period
Understand the importance of close monitoring in recovery
Create a post-operative plan tailored to each individual patient
Feel confident to create discharge instructions for your patient
Confidently communicate with the owner about the anaesthesia and surgery the patient has received
Perform a thorough physical post-operative check, including the whole patient
Understand the best dental care an owner can provide at home, along with alternative options if these goals cannot be met
The course will be fully tutored by Stacey Parker and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
february 3 (Monday) – 28 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Stacey ParkerISFM Cert(FN), NCert (Anaes) & (Dent), AdvNCert (Anaes), LVNP (Anaes), RVN Dental Nurse, Perry Dental Referrals

Course Details
Nurses at both general practice and referral level will commonly nurse patients with endocrine disease throughout their career. Understanding the basic concepts of endocrinology means nurses can apply
Course Details
Nurses at both general practice and referral level will commonly nurse patients with endocrine disease throughout their career. Understanding the basic concepts of endocrinology means nurses can apply knowledge to their care in order to better support their patients.
Having an understanding of the pathophysiology of common endocrine diseases, as well as the tests performed means that we can become a useful support in clinical decision making, which subsequently improves job satisfaction and allows us to nurse to our full potential.
Each week we will look at a different endocrine disease in the cat or the dog. Following the course you will have refreshed your underpinning knowledge of the endocrine system in the canine and feline patient to include the chemical messenger and feedback systems, the types of endocrine diseases commonly affecting our patients, the tests we use and how these diseases impact our nursing care.
Week 1
Canine Hypothyroidism
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify the clinical signs of canine hypothyroidism
Explain the role of hormones in the body
Explain the relationship between TSH and thyroid hormones
Describe what canine hypothyroidism is and why it occurs
Describe ways to support the client owning a canine with hypothyroidism
Week 2
Canine and Feline Diabetes
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Name the 3 types of cell that contribute to the endocrine function of the pancreas
Name the two main types of insulin used in cats and dogs
Describe the reason dogs become diabetic
Describe the reason cats become diabetic
Explain some differences in the nursing considerations you would give cats compared to dogs and why
Week 3
Feline Acromegaly
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Identify 3 major hormones that are lost when you remove the anterior pituitary gland
Explain how feline hypersomatotropism occurs
Discuss how excess growth hormone results in acromegaly
Explain the nursing considerations for a hypophysectomy patient
Explain the support that a client might need for a cat with FeHS
Week 4
Feline Hyperthyroidism
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Discuss the clinical signs that a hyperthyroid cat might present with
Explain the effects of too much thyroid hormone on the body
Demonstrate an understanding of the treatment options available for the disease in order to support the client with the hyperthyroid cat
Describe the most commonly used test to diagnose feline hyperthyroidism and what that test is measuring
Explain the difference between free T4 and total T4
Week 5
Canine Hyperadrenocorticism (Cushing’s Disease)
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Explain the reasons why canine hyperadrenocorticism (HAC) occur
Identify the clinical signs associated with a canine HAC patient
Discuss some of the common tests available for HAC and the reasons for their use
Identify 3 main forms of treatment for the canine HAC patient
Demonstrate an understanding of the nursing considerations for the patient with HAC
Week 6
Canine Hypoadrenocorticism (Addison’s Disease)
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Explain the causes of canine hypoadrenocorticism
Identify some of the clinical signs that a patient may present with and why
Discuss the treatment options available to the client with the hypoadrenocorticism pet
Demonstrate an understanding of the nursing considerations for a canine with hypoadrenocorticism
Name some of the tests that a vet may ask you to carry out on the suspected hypoadrenocorticism patient and discuss why they may be required
The course will be fully tutored by Gina Parkes and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case scenarios, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
February 3 (Monday) – March 14 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Gina ParkesDipAVN(Small Animal), PgCert(Ved Ed), FHEA, RVN Head Medicine Nurse, Royal Veterinary College

Course Details
Week 1 Nutrition and Husbandry at Home Dietary requirements Environmental needs Incorrect feeding problems Obesity Tempting rabbits to eat hay Learning objectives After completion of this week, participants should be able
Course Details
Week 1
Nutrition and Husbandry at Home
Dietary requirements
Environmental needs
Incorrect feeding problems
Obesity
Tempting rabbits to eat hay
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Discuss the nutritional requirements of rabbits and why these are important
Recognise problems related to incorrect or poor diet and the implications these have on health and welfare
Appreciate that rabbits need large enclosures, which allow them to exhibit normal behavioural patterns. These are important from a health and welfare perspective. We will examine what rabbits need to be happy
Understand obesity and how to implement a weight loss programme for rabbits
List various methods to encourage picky rabbits to eat hay!
Week 2
Preventative Healthcare
Neutering – when and why
Vaccination – myxomatosis, RVHD1 and RVHD2
Endo and ectoparasites
Flea treatment
Worming treatment
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the best time to neuter rabbits
Appreciate why we should be neutering all rabbits – health, welfare and behavioural benefits
Know all the latest vaccination information and background on these fatal viruses
Know which endo and ectoparasites can affect rabbits and the clinical signs
Discuss if rabbits require prophylactic flea and worm treatment, and if so, when?
Week 3
Implementing Rabbit Clinics and Client Evenings in Practice
Setting up rabbit clinics
Running client evenings
What to discuss
Health checking
Benefits to the practice
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand that client education is imperative but there is more than one way to deliver this
Discover the benefits of both rabbit clinics and client evenings
Know what should be discussed and the clinical examination to help detect problems
Appreciate why being a rabbit friendly practice is of benefit to you!
Week 4
Common Medical Diseases
Gastrointestinal stasis and blockages
Dental disease
Urinary tract disease
E. cuniculi
Myxomatosis and RVHD
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe the common conditions that rabbits present to veterinary practices and require hospitalisation
Ascertain if a rabbit has gastrointestinal stasis or a blockage – differences and treatments
Identify clinical signs and causes
List the treatment options
Describe preventative measures to help ensure rabbits remain healthy
Week 5
Rabbits in the Practice
Reducing stress
Hospitalisation
Gold standard rabbit nursing
Medicating
Fluid therapy and blood sampling
Supportive feeding
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand that everything that we do to rabbits whilst they are hospitalised induces some degree of stress. Learn ways to reduce this, which are easily achieved in practice
Appreciate that hospitalised rabbits can require in-depth care which can be daunting. Learn how to effectively nurse rabbits to ensure optimum care
Learn how to medicate rabbits in an effective and safe manner is imperative, as well as how to syringe feed, deliver fluid therapy and acquire successful blood samples with minimal stress to the rabbit or nurse!
Week 6
Rabbit Anaesthesia and Analgesia
Signs of pain
Analgesia options
Making rabbit anaesthesia safer
Monitoring under general anaesthesia
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Review rabbit anaesthesia and learn how to build up your confidence, including pre op, intra op and post op care. Anaesthetising rabbits can be overwhelming but doesn’t need to be!
Know the clinical signs rabbits show when they are in pain, and learn how to use the Rabbit Grimace Scale
Review the analgesics available for rabbit medicine
Understand the parameters monitored during anaesthesia – including CO2, SPO2,reflexes, HR, RR and BP readings
The course will be fully tutored by Claire Speight and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
February 17 (Monday) – March 28 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Claire SpeightA1 Clinical Coach, C&G Cert Nursing Exotic Species, RVN Senior Nurse, Kettering Vets4Pets
Course Details
It is estimated that one in three companion animals will die of cancer, which makes understanding the disease and caring for these animals and their families common within
Course Details
It is estimated that one in three companion animals will die of cancer, which makes understanding the disease and caring for these animals and their families common within our role. Despite this demand, there is limited space in the veterinary nurse curriculum dedicated to cancer and so here we explore the subject in more practical detail.
This course discusses how cancer manifests in the companion animal, how a cancer diagnosis is made and how chemotherapy treatments are administered. Throughout the weekly sessions there are activities and opportunities to test your learning and evaluate how you could introduce some of the practical elements into your practice.
After completing this 4 week online course, the participants will have a greater knowledge and understanding of the basic principles of veterinary oncology and be able to apply this to their own working practices.
Week 1
What is Cancer?
Pathophysiology of neoplasia
Common causes of cancer in animals
Classifications of cancer types
The difference between benign and malignant disease
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand the alterations in the cell cycle that results in neoplastic disease
List the different types of cancer based on tissue origin
Describe the different causes of cancer in small animals
Explain how benign disease is different to malignant disease and the risks associated with both conditions
Identify higher risk categories of patients and analyse the research available in line with evidence-based medicine
Week 2
Diagnosis and Prognosis
Fine needle aspirates
Cancer cytology
Cancer staging
Specialist tests for cancer
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
List fine needle aspirate methods to optimise cytological yield
Evaluate a cytology sample in-house to ensure sample is of diagnostic quality
Understand the commonly preferred methods for staging patients with neoplasia
Describe the types of specialist tests required to further categorise cancer
Analyse personal skill set and determine if any modifications to current practice would be beneficial
Week 3
Common Chemotherapy Agents
Overview of common chemotherapy drugs
Administering chemotherapy
Chemotherapy safety
Adverse effects with administering chemotherapy
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand how chemotherapy agents work
Explain how to correctly administer chemotherapy agents
List what safety factors should be observed when administering chemotherapy in practice
Describe how to manage an extravasation injury and reduce risk of chemotherapy associated nausea and vomiting
Evaluate practice protocols to standardise and promote best practice in line with most current information
Week 4
Client and Patient Support
Introduction to oncology clinics
Nadir checks
Managing adverse effects following chemotherapy administration
The Cancer Journey
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Describe how and why a nadir check is performed
Identify common adverse effects associated with chemotherapy
Understand preventive and interventional treatment protocols for chemotherapy associated adverse effects
Explain the causes for likely outcome of treatment failure and the physiology behind this
Reflect over professional skill set and evaluate how you can further enhance your personal development to support clients of patients with cancer
The course will be fully tutored by Nicola Read and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
February 24 (Monday) – March 21 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Nicola ReadDipAVN (Medical), PgCert Veterinary Oncology, AFHEA, RVN Head Oncology Nurse, Royal Veterinary College
march 2025
Course Details
As veterinary nurses, we want to provide our patients with the best possible care that we can and it’s hard to see our patients suffering and in pain.
Course Details
As veterinary nurses, we want to provide our patients with the best possible care that we can and it’s hard to see our patients suffering and in pain. Luckily our profession allows us to prevent this in many ways, but are we tackling pain the right way and making the best choices for analgesia? Can we make improvements to help our patients remain pain free and reduce side effects of the therapies we choose – whether that’s for our patients in the clinic or at home?
In order for us to treat and manage pain in our patients, we first need to understand the physiology behind how animals feel pain. We will start by expanding our knowledge and understanding of the pain pathway, before moving on to the different analgesia options for acute and chronic pain conditions. We will finish the course with pain scoring. By the end of the 4 weeks, we will have overviewed pain and the different treatment options available with the hope, that alongside the veterinary surgeon, we can build patient specific multi-modal analgesia plans for all our patients.
Week 1
The Physiology of Pain
Pain definitions
The mammalian pain pathway
Different types of pain
Principles of analgesia
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Outline the definition of pain and associated terminology
Describe the different stages of the pain pathway and sites for analgesia intervention
Understand the concept of multi-modal analgesia and pre-emptive analgesia
Week 2
Analgesia for the In-patient
Review the analgesia agents used to treat acute pain conditions:
Opioids
NMDA antagonists
Local anaesthetics
Alpha 2 agonists
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Be familiar with the different systemic and local options for treating acute pain
Discuss balanced multi-modal analgesia plans for patients in the veterinary practice
Understand the mechanisms of action, effects and side effects of the listed analgesic agents
Week 3
Analgesia for the Out-patient
Review the analgesia options for managing pain on a longer term basis:
NSAIDs
Paracetamol
Tramadol
Gabapentin
Alternative therapies
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Be familiar with the different systemic and alternative therapies for treating chronic pain
Discuss balanced multi-modal analgesia plans for patients at home
Understand the mechanisms of action, effects and side effects of the discussed analgesic interventions
Week 4
Pain Assessment Methods
Review the different pain scoring options for both in-patients and out-patients
Canine pain scales
Feline pain scales
Grimace scales
Chronic pain scales
Pitfalls and problems with pain assessment
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Have a better understanding of the different pain assessment types
Appreciate where pain assessments can be beneficial for managing conditions and allowing for appropriate analgesia interventions in the hospitalised patient
Provide owners with the tools to monitor and assess their pet’s pain and quality of life at home
Describe the indications and contraindications for pain scoring
The course will be fully tutored by Lisa Angell, and will consist of 10 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 4 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
march 3 (Monday) – 28 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Lisa AngellVTS (anaesthesia and analgesia) PgCert Vet Ed, FHEA, RVN Head Anaesthesia Nurse, Royal Veterinary College
may 2025
Course Details
Week 1 What is an Anaesthesia Plan? How to construct an individual anaesthesia plan Common anaesthesia-related complications What you need to know about the drugs Very old and very young patients
Course Details
Week 1
What is an Anaesthesia Plan?
How to construct an individual anaesthesia plan
Common anaesthesia-related complications
What you need to know about the drugs
Very old and very young patients
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Construct an individualised anaesthesia plan
Understand common anaesthesia and surgery related complications
Appreciate the important effects and side effects of drugs commonly used in the peri-anaesthetic period
Understand specific considerations for geriatric and paediatric patients
Week 2
The Anaesthetist’s Worst Nightmares!
Brachycephalic dogs
Obese patients
Care! Difficult temperament
Some endocrine and medical conditions
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Provide safe anaesthesia for brachycephalic and obese patients
Understand how to anaesthetise ‘aggressive’ dogs safely
Understand the priorities for sick patients and those with concurrent disease
Week 3
Let’s get Cutting – Abdominal Surgery
Anaesthetic considerations for laparotomy and laparoscopy
Case examples
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Provide analgesia and local anaesthesia for abdominal surgery
Understand the effects of laparoscopy on the patient’s physiology and how to manage them
Discuss the considerations for some particular examples of abdominal surgery
Week 4
Heart and Lungs
Anaesthetic considerations for respiratory disease and thoracic surgery
Anaesthetising patients with common cardiac diseases
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Know the requirements of patients with intra-thoracic disease
Understand how to manage a patient undergoing a thoracotomy
Appreciate the basics of controlled ventilation
Provide analgesia and local anaesthesia for thoracic surgery
Manage patients with common cardiac diseases
Week 5
Eyes, Brains and Spines
Anaesthetic considerations for neurology and ophthalmology patients
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand practical and physiological considerations for ocular surgery
Explain the basics of neuromuscular blockade
Know how to provide analgesia and local anaesthesia for spinal surgery
Identify the pathophysiology of intracranial disease and how to manage it
Understand the particular difficulties of anaesthesia for magnetic resonance imaging
Week 6
Bringing it all Together – Case Examples
Complex procedures and sick patients, plus some orthopaedic procedures
Learning objectives
After completion of this week, participants should be able to:
Understand how to combine patient and procedure related requirements
Construct advanced anaesthesia plans
Understand how to prioritise the importance of different anaesthetic considerations
Provide analgesia and local anaesthesia for some orthopaedic procedures
This course will be fully tutored by Colette Jolliffe and will consist of 15 hours of CPD given in various formats, including tutorials, tasks, case studies, forum discussions and quizzes. This course is tutored for 6 weeks, followed by a two week extension of untutored ‘catch up’ time, before the course officially ends.
All delegates will then have unlimited lifetime access to the learning material for future reference
Time
May 5 (Monday) – June 13 (Friday)
Location
Online
Speaker
Colette JolliffeBVetMed, CertVA, DipECVAA, FRCVS European and RCVS Recognised Specialist in Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia, Anderson Moores Veterinary Specialists

Online CPD for Vet Nurses
Excel CPD specialises in providing online CPD for veterinary nurses and technicians all over the globe. Our courses are also fully approved by AVNAT for our nursing colleagues in Australia and New Zealand.